5 key facts about this project
# Analytical Report on the Architectural Design Project: House of the Future, Dubai, UAE
## Overview
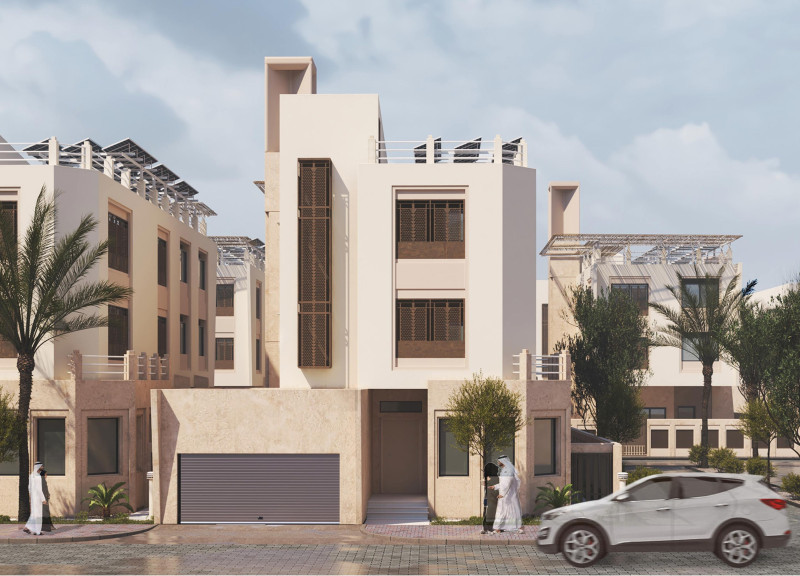
Located in Dubai, UAE, the House of the Future exemplifies a design approach that interweaves elements of traditional Emirati culture with contemporary architectural practices. The project aims to offer a modern living environment while honoring regional heritage and prioritizing sustainability and adaptability. Inspired by the traditional dhow boat, the design reflects a metaphorical journey toward innovation, integrating aspects of form and function that resonate with the area's cultural significance.
## Material Composition and Architectural Features
### Materiality
The selection of materials plays a crucial role in the project’s identity, as it seeks to establish a dialogue with its surroundings:
- **Reinforced Concrete**: Utilized for its structural integrity and flexibility, this material forms the backbone of the design.
- **Natural Stone**: Serving as a key façade element, natural stone contributes to the visual continuity with the local environment while conveying a sense of permanence.
- **Wood**: Incorporated in shading devices and interior applications, wood adds warmth and a connection to traditional craftsmanship.
- **Glass**: Expansive glass windows enhance natural light and promote a visual connection to the outdoors, optimizing the user experience.
These materials are chosen not only for their durability but also for their alignment with the aesthetic language of the region.
### Form Generation and Functional Layout
The architectural form emerges through a systematic process that emphasizes functional zoning and sustainability:
1. **Functional Zoning**: The initial organization of spaces supports an effective flow, differentiating public and private areas.
2. **Extruded Masses**: The design evolves through the extrusion of primary forms to articulate social and private zones distinctly.
3. **Windcatcher Feature**: This architectural element plays a vital role in enhancing natural ventilation, effectively reducing reliance on mechanical cooling systems.
4. **Aerodynamic Enhancements**: The chamfering and tapering of forms contribute to both visual interest and improved airflow.
5. **Sustainable Systems**: The roof is equipped with solar panels, and green roofs are integrated, reflecting an operational commitment to reducing environmental impact.
### Urban Context and Community Engagement
The urban layout is informed by a contemporary interpretation of traditional Emirati urbanism, utilizing the **Sikkak planning system**. This configuration of plots promotes enhanced airflow and supports community interactions. The design facilitates a walkable neighborhood, integrating shared spaces that encourage social connections among residents.
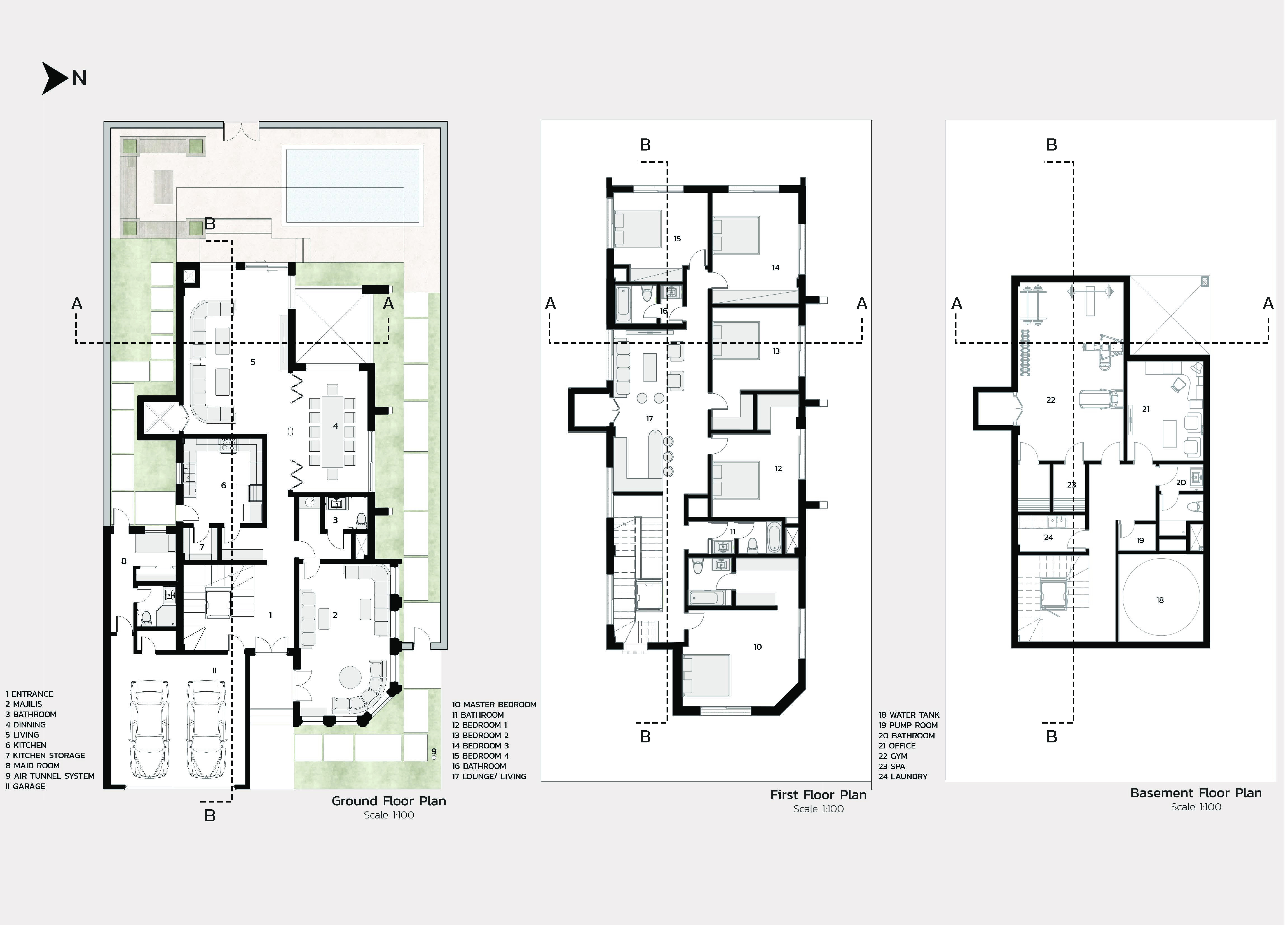
The floor plans are crafted to enhance functionality:
- **Ground Floor**: Contains essential amenities, including a garage and interconnected living spaces, optimized for daily living.
- **First Floor**: Dedicated to private quarters with bedrooms and communal lounge areas, fostering family interaction.
- **Basement Floor**: Serves as a utility area equipped with features such as offices, a spa, and laundry facilities, providing additional flexibility.
Incorporating these diverse components, the House of the Future seeks to harmonize private and communal living, addressing the evolving needs of its inhabitants while promoting a collective community spirit.