5 key facts about this project
### Overview
Located in the Al Qudra Desert of Dubai, the House of the Future serves as a contemporary architectural model that harmonizes modern living with ecological responsibility. This initiative showcases a thoughtful integration of traditional Bedouin concepts within a framework designed to respond to the surrounding desert environment, prioritizing sustainability, innovation, and cultural resonance.
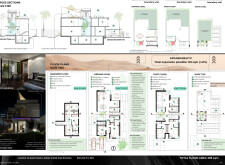
### Spatial Organization
The residential layout is strategically developed across three levels—basement, ground floor, and first floor—on a 15x30 meter plot with an expansion capability of up to 123 sqm. The basement is designed for functionality, encompassing a heavy cooking kitchen, staff accommodations, and storage space. The ground level features interconnected living and dining areas that open to the outdoor environment, as well as a flexible gym/office space and necessary utility facilities. The first floor accommodates private areas, including a master suite and two additional bedrooms, complemented by a balcony that enhances both living space and outdoor interaction.
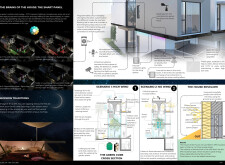
### Material and Energy Efficiency
Material selection plays a crucial role in maintaining the project’s sustainability objectives. The employment of locally sourced and environmentally conscious materials reduces the carbon footprint. Prefabricated walls expedite construction while minimizing waste. The roof integrates solar panels for energy generation, supported by lightweight yet durable aluminum and steel structural components. The use of concrete and plaster provides thermal mass, optimizing passive heating and cooling strategies.
### Advanced Sustainable Solutions
In response to water scarcity, an advanced irrigation system utilizes rainwater collected via the Wind Tower, which also serves as a natural cooling mechanism. The project is powered by a combination of solar energy and wind turbines, with a battery system in place to store excess energy. Additionally, smart home technology includes a centralized Smart Panel that controls climate, lighting, and security, allowing for adaptive responses to environmental conditions and occupancy.
### Community Engagement
Landscape design incorporates native plants, such as date palms and bougainvillea, which enhance the aesthetic appeal while requiring minimal water. Communal spaces, or Majlis, foster social interactions and encourage cultural continuity, providing a modern response to traditional community gatherings.