5 key facts about this project
# Architectural Design Report: House of the Future, UAE
## Project Overview
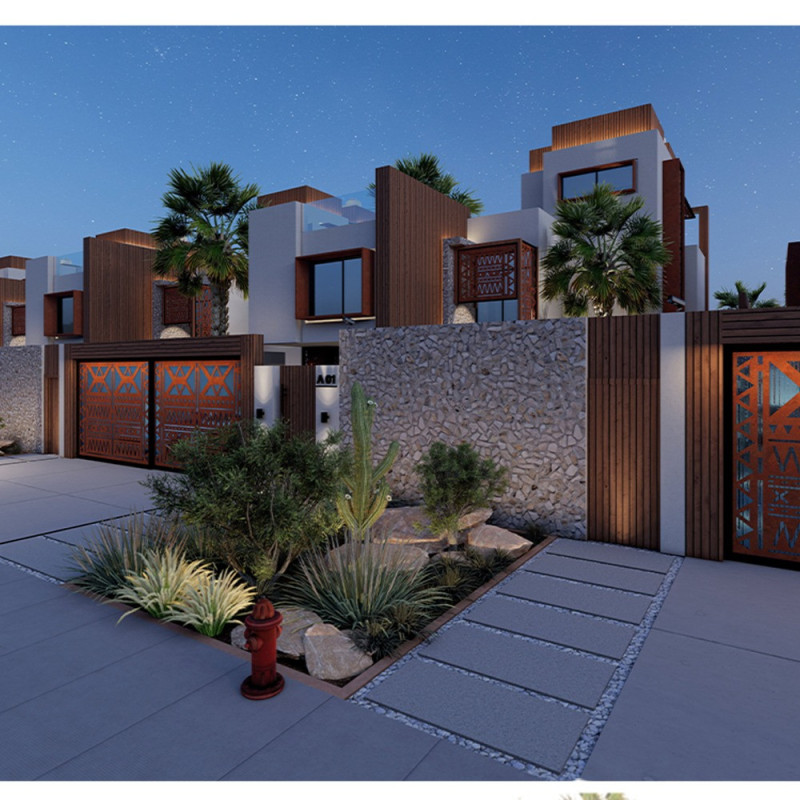
Located in the UAE, the House of the Future is a contemporary residential structure that integrates traditional design elements with sustainable practices. Covering a plot size of 450 m², the building spans a total floor area of 300 m². The intent of the design is to enhance the quality of life for residents through innovative architectural solutions that prioritize environmental efficiency.
## Spatial Strategy and User Experience
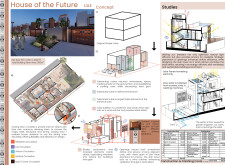
The design employs a modular cubist approach, beginning with a fundamental cubic form from which various architectural components have been manipulated. This strategy effectively reduces unnecessary space while ensuring shade at the ground level and establishing a dedicated parking area to minimize heat gain, which is essential in the region's climate. A clearly defined entrance is achieved through the subtraction of a cube, creating a welcoming entryway that enhances visitor experience.
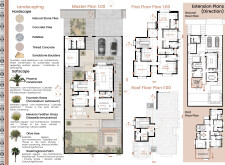
The internal layout is meticulously planned to facilitate efficient circulation for residents, visitors, and service personnel. Separate entrances for different user groups enhance privacy and promote a functional flow throughout the space. The arrangement of common areas allows for flexible use, fostering interaction among family members and guests.
## Materiality and Sustainability
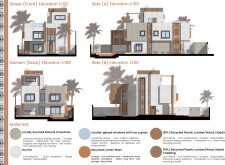
Material selection focuses on sustainability and local identity. Locally sourced natural limestone provides thermal insulation and durability against local climate conditions, while recycled corten steel enhances building longevity and energy conservation. Recycled plastic lumber used for wood cladding furthers sustainability efforts by employing a closed-loop recycling process.
The incorporation of double-glazed windows with low-emissivity glass optimizes insulation and reduces UV exposure and noise pollution. Additionally, the project utilizes natural stone tiles, concrete, and culturally significant flora, such as Phoenix canariensis and Fountain Grass, to enhance the ecological footprint of the landscape while providing aesthetic value.
Architectural innovations include strategic opening placements that optimize air circulation and privacy, alongside systems for rainwater collection and greywater recycling, promoting water conservation. The use of solar panels contributes to a regenerative energy model, underscoring the commitment to sustainable living practices.