5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
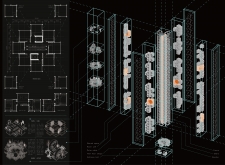
Located in Hong Kong, the "Upside-Down Machine" is a residential development that seeks to address the challenges of space utilization, community interaction, and environmental integration within a densely populated urban context. The design emphasizes a modular approach, typologizing residential units as individual components that together create a cohesive and adaptable living environment. This configuration aims to enhance social connections among residents while reflecting the complexities of modern urban life.
## Spatial Strategy and User Interaction
The project features an intricate spatial organization, with modular units strategically arranged within a defined structural framework. Each unit is oriented to maximize natural light and airflow, contributing to vibrant and livable spaces. The layout includes shared communal areas, such as gardens and activity halls, designed to facilitate interaction among occupants while maintaining necessary privacy for individual units. Vertical connectivity is emphasized through strategically placed stairs and elevators, encouraging ease of movement and engagement throughout the structure. The incorporation of terraces and green spaces within the design ensures the presence of natural elements, providing residents with communal areas for relaxation and recreation.
## Material Selection and Sustainability
The material palette is carefully chosen to balance aesthetics with functionality. A steel framework lends structural integrity while allowing for design flexibility. Expansive glass paneling enhances views and invites natural light into living areas. Concrete serves as a durable foundation, ensuring the building’s resilience in an urban environment. Green roof systems are integrated to manage stormwater and improve insulation, contributing to the building’s environmental performance. Additionally, features such as natural ventilation and water recycling technologies reflect a commitment to sustainability, showcasing innovative strategies for minimizing ecological impact. The diversity of unit types accommodates varying household compositions, thus promoting inclusivity and catering to a broad demographic spectrum.