5 key facts about this project
### Overview
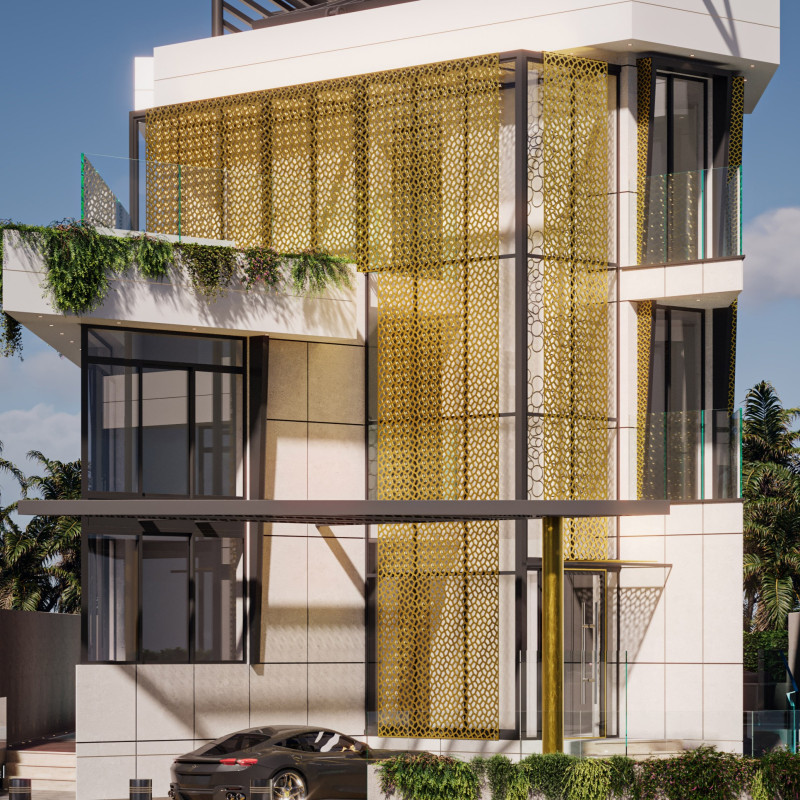
Located in Dubai, the residential project emphasizes a modern approach to architecture that merges advanced construction techniques with sustainable practices, while also considering local cultural contexts. The design aims to create a flexible living environment that can adapt to the evolving needs of its inhabitants. The integration of modular construction and innovative technologies positions the project as a forward-thinking model for contemporary residential living.
### Modularity and Spatial Strategy
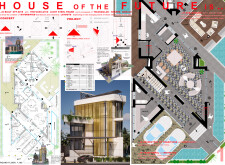
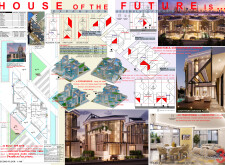
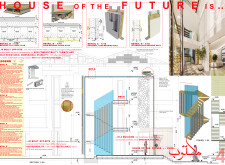
The building employs a modular design, utilizing prefabricated light steel frames and triangular-shaped modules. Each basic module has an area of 16.0 m² and can be arranged in various configurations to optimize space utilization. This adaptability allows for future expansion, enabling homeowners to modify their living arrangements as necessary.
The layout is structured to balance communal and private spaces effectively. The ground floor features open-plan areas for social interaction, including a living room, dining area, and kitchen, which connect seamlessly with an outdoor pool. In contrast, the first floor is dedicated to private quarters, such as bedrooms and workspaces. The design also incorporates upper levels for potential expansion, integrating terraces and balconies that facilitate leisure activities and enhance the overall living experience.
### Sustainable Material Choices
The selection of materials is crucial to both the aesthetic and environmental performance of the dwelling. Cold Formed Steel (CFS) is utilized for the framework, providing durability and stability, while high-quality thermal insulation materials are applied to enhance energy efficiency. The design also incorporates recycled materials, including reclaimed wood, in an effort to reduce the overall environmental impact.
Reflective paint is used on external walls to minimize heat absorption, further contributing to indoor climate control. Additionally, a green roof system is integrated into the design, promoting biodiversity while improving insulation and managing stormwater. These material choices underscore a commitment to sustainability and a reduced ecological footprint throughout the building's lifecycle.