5 key facts about this project
### Overview
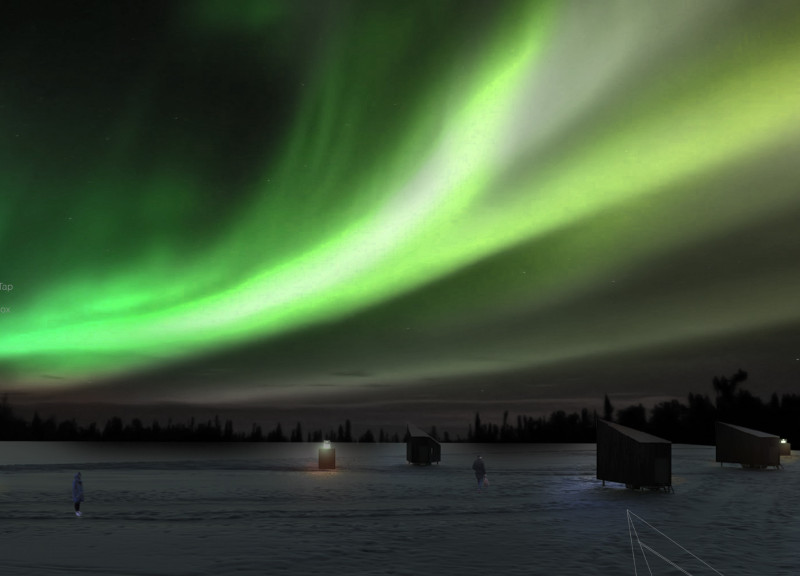
Located near Mývatn Lake, this architectural design project seeks to harmonize with the unique landscape of Iceland while honoring its cultural heritage. The approach emphasizes sustainable living within a challenging environment, utilizing innovative strategies to enhance both functionality and aesthetic appeal.
### Structural and Spatial Strategy
The design is characterized by angular and geometrical forms, reflective of Iceland's natural contours. The overall silhouette consists of triangular and polygonal facets, enhancing structural stability and addressing practical climatic concerns such as snow and wind loads. Large windows integrate the interiors with expansive views of the Northern Lights, establishing a direct dialogue with the surrounding landscape. The modular configuration of the cabin units promotes reconfiguration based on seasonal needs, supporting a flexible use of space that aligns with a sustainable lifestyle.
### Material Selection
A careful choice of materials reinforces the project’s sustainability goals and suitability for the climate. Key materials include sustainably sourced wood for its insulating properties, a steel frame providing structural integrity, and eco-friendly OSB sheathing for wall panels. The incorporation of thermal insulation ensures energy efficiency, while large glass windows maximize natural light and reduce reliance on artificial lighting. Additionally, geothermal heating systems and innovative waste management solutions, such as composting toilets, are integrated into the design to further enhance its sustainability profile.
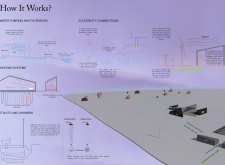
### Environmental Systems
The project employs renewable energy resources, including wind turbines and local grid connections, as part of its comprehensive strategy for energy efficiency. Water systems are designed to utilize Mývatn Lake as a primary source, incorporating a filtration and pumping system that reflects a commitment to preserving local ecosystems. The spatial arrangement encourages interaction with nature while fostering a sense of community through shared outdoor spaces, such as a wooden deck that connects various units and enhances the overall user experience.