5 key facts about this project
### Overview
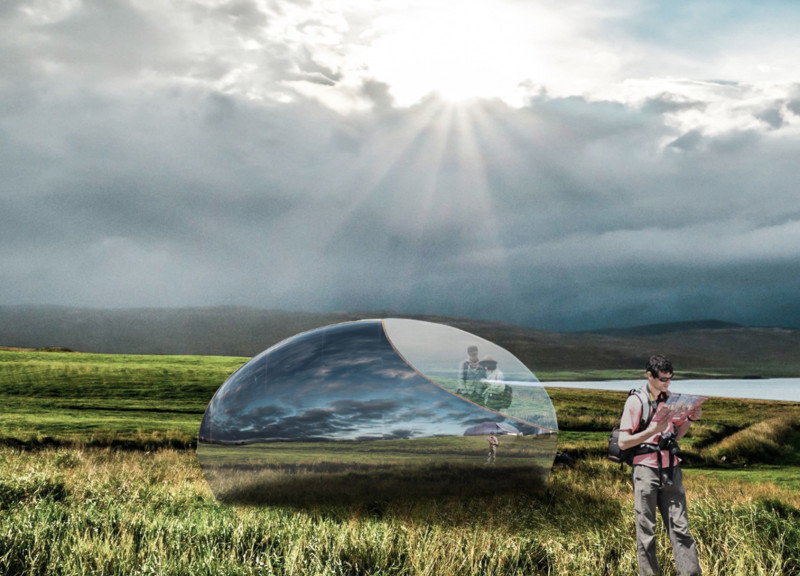
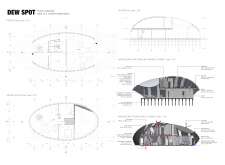
Located in Iceland, near the Kiy Myvatn and Herðubreið volcanoes, the project introduces mobile hotel capsules designed as observatories for guests, aligning the built environment with the natural landscape. The intent of the design is to create a facility that enhances the surrounding beauty while adhering to principles of sustainability and ecological integration.
### Spatial Strategy and User Experience
The design incorporates a flexible internal layout that optimizes space efficiency, featuring multi-functional furniture that serves as sleeping and observation areas. Each capsule is equipped with natural ventilation systems to improve air circulation, reducing reliance on mechanical cooling. Additionally, integrated technologies, including geothermal heating and solar panels, facilitate energy efficiency throughout the facility.
### Material Considerations and Sustainability
Material selection is paramount to ensure both aesthetic integration and environmental responsibility. The structure utilizes zinc-polished cladding for its reflective qualities and durability, while triple-glazed windows provide thermal efficiency without sacrificing natural light. The use of recyclable galvanized steel for the framework, along with clay for thermal mass and cross-laminated timber for structural performance, underscores a commitment to sustainable building practices. Rainwater collection tanks further reinforce the project's ecological approach, highlighting its role as a model for responsible tourism development.