5 key facts about this project
## Architectural Analysis Report for the Ghaf Project
### Overview
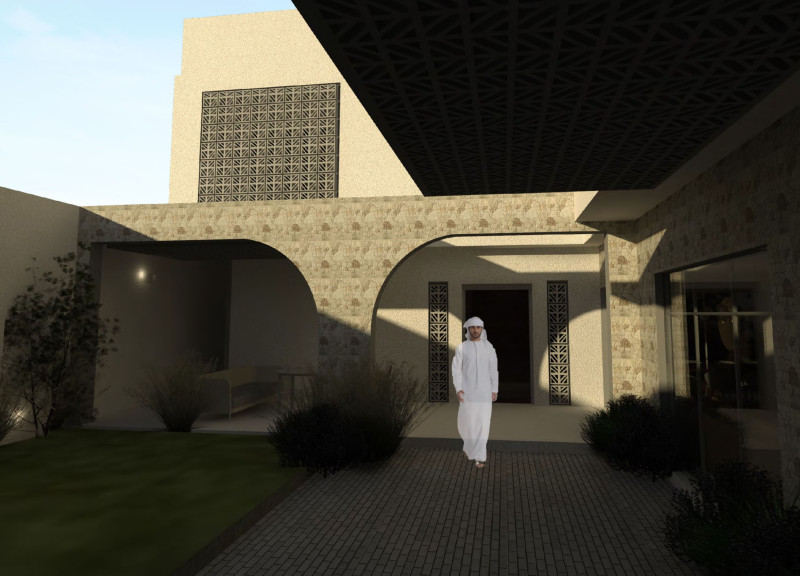
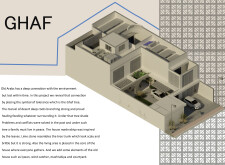
Located in the UAE, the Ghaf project engages with regional cultural heritage while addressing contemporary living requirements. Inspired by the Ghaf tree, a symbol of resilience in Arab societies, the design emphasizes the connection between built environments and their natural surroundings. The project aims to foster community interaction and environmental harmony through a thoughtful architectural framework.
### Layout and Spatial Strategy
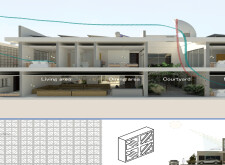
The overall design features a symmetrical configuration that revolves around a central courtyard, reflecting traditional Middle Eastern residential architecture. The strategic zoning of spaces creates a balance between public and private areas, facilitating social interactions while ensuring privacy. Key components of the layout include a living area that promotes communal engagement with visual access to the courtyard, a dining area designed for family gatherings, and a master bedroom positioned to receive ample natural light while being secluded from high-traffic zones.
### Materiality and Environmental Considerations
The choice of materials is integral to the project’s sustainability and regional relevance. Local lime stone, aerated concrete, and glass-reinforced concrete (GRC) are utilized, offering durability, energy efficiency, and aesthetic value. The design incorporates traditional mashrabiya elements, enhancing privacy and allowing for natural light and airflow. Furthermore, passive cooling and heating strategies are maximized, featuring wind catchers and strategically placed solar panels to reduce dependence on mechanical climate control. This thoughtful integration addresses both environmental impact and the climatic conditions of the area.