5 key facts about this project
# Architectural Design Report: House of the Future
## Overview
The House of the Future is located in an undefined urban setting, designed to integrate sustainability, cultural resonance, functionality, and contemporary aesthetics. This project aims to create a living environment that promotes energy efficiency and human connectivity to nature while reflecting the heritage of the region.
## Spatial Configuration
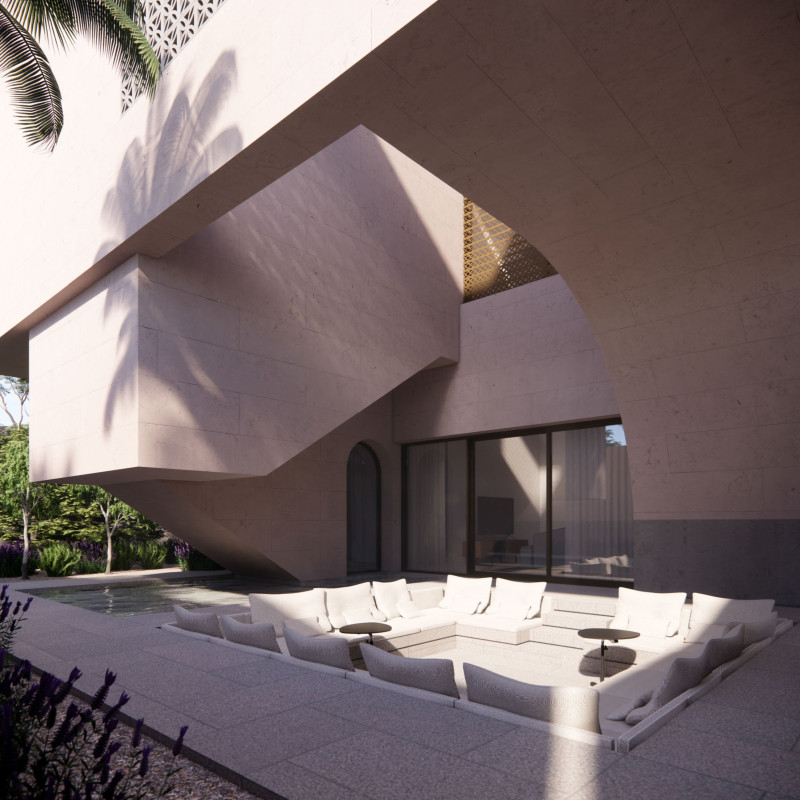
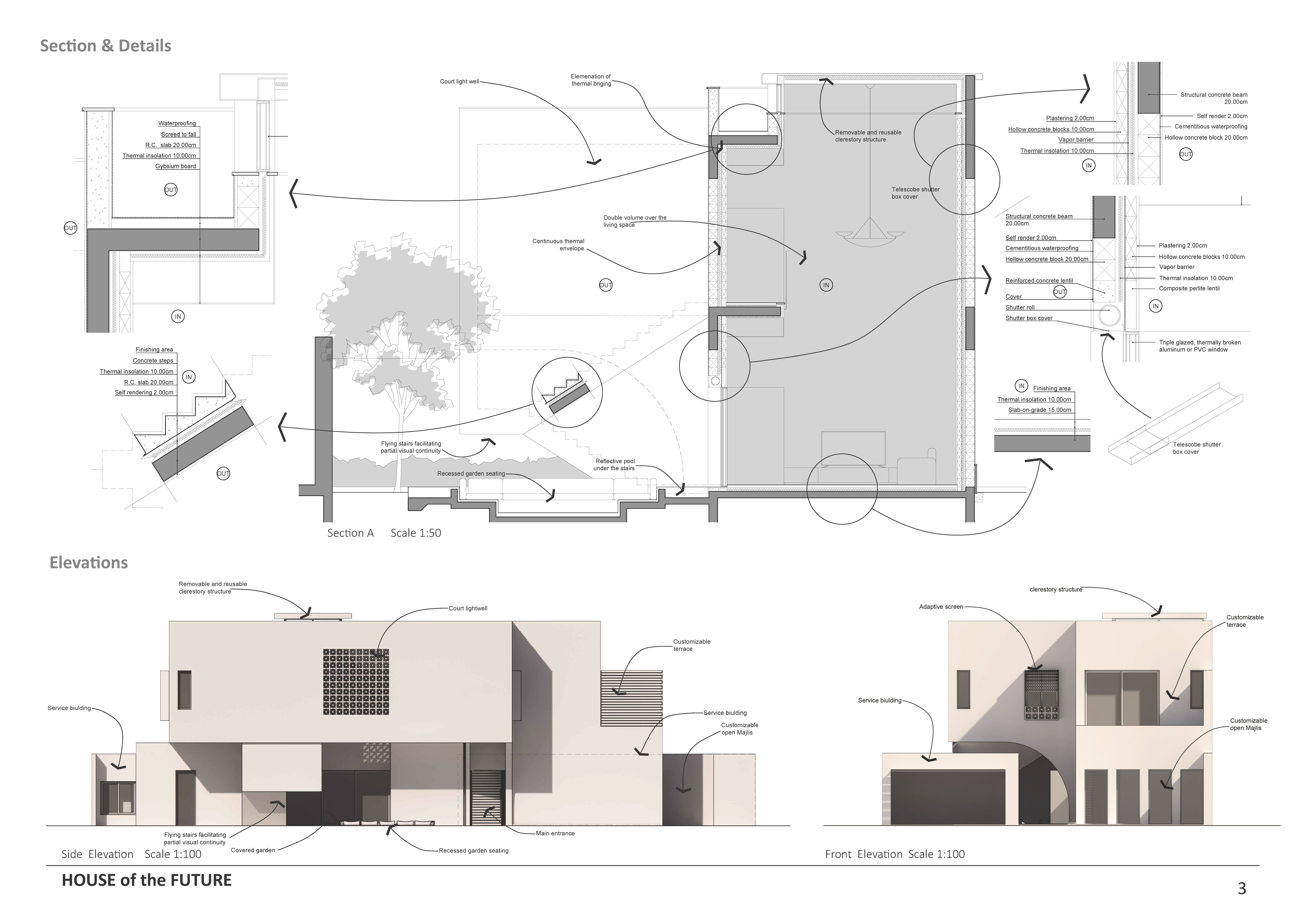
The spatial organization draws inspiration from traditional Emirati design, emphasizing the creation of intimate spaces that foster community. The layout features a central *housh* (courtyard) that provides a communal area under the upper floor, effectively blending indoor and outdoor experiences. The ground floor includes multifunctional spaces that accommodate both family activities and formal gatherings, ensuring privacy without sacrificing openness. The first floor introduces a suite and additional bedrooms designed for optimal natural ventilation and views, enhancing both comfort and interaction among family members.
## Sustainable Materiality
The selection of materials for the project underscores a commitment to sustainable and visually appealing construction. Notable materials include manufactured stone for durability, plaster for thermal mass, anodized aluminum for window and shading elements, and wood composite for landscaping features. Native vegetation, such as Moringa Oleifera and Lavandula Pubescens, is integrated into the landscape design to support local biodiversity and establish a harmonious relationship between the inhabitants and the environment.
The building's structural integrity is achieved through four main load-bearing walls, allowing for a flexible interior layout that can adapt over time. Key sustainability features include passive solar design elements, energy harvesting systems, and natural ventilation strategies, reducing reliance on mechanical systems and enhancing comfort throughout the changing seasons.