5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
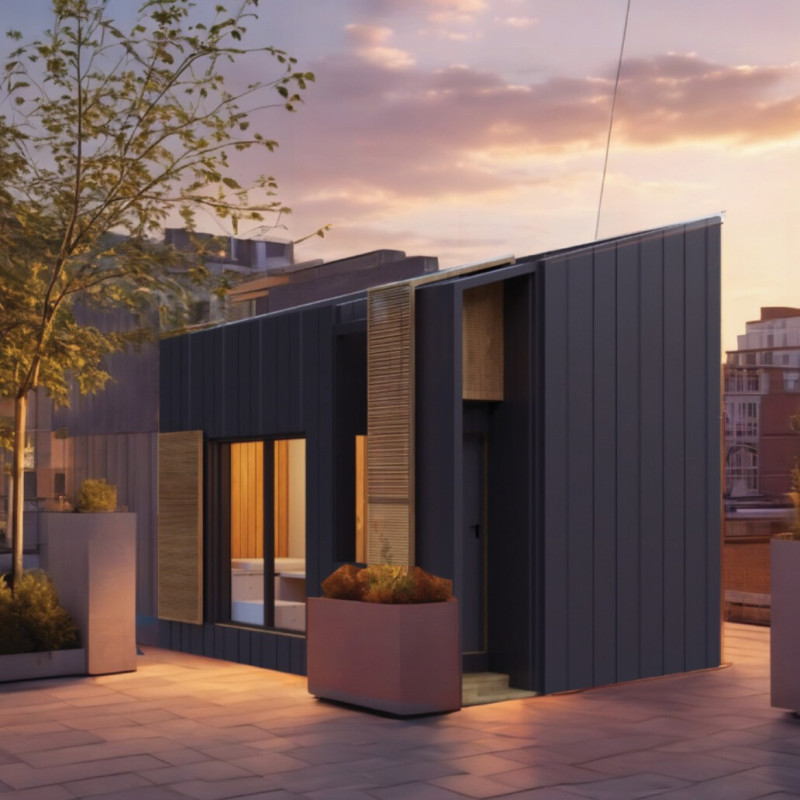
The METRON Airspace Micro-communities project is located in Camden, Greater London, and aims to address contemporary urban housing challenges through innovative micro-living solutions. This development emphasizes ecological sustainability and adheres to the Passivhaus standard, which enhances energy efficiency and reduces environmental impact.
### Spatial Efficiency
The design features compact living spaces optimized for functionality, with a floor area of 17.86 m² (approximately 24.95 m² total). Each micro-home adopts a boxy shape to facilitate an efficient layout. Modular construction techniques are utilized, allowing for quick assembly while maintaining quality. The monochromatic facade, primarily composed of dark materials, establishes a modern aesthetic that contrasts with the natural environment.
### Sustainable Material Selection
The construction employs a range of sustainable materials to support its ecological goals, including:
- **Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)** for structural components, chosen for its low carbon footprint.
- **Kingspan QuadCore Panels** that provide superior insulation and thermal performance to minimize energy consumption.
- **Hybrid Timber/Aluminium Windows** that enhance durability and thermal efficiency, crucial for compliance with Passivhaus standards.
- **Perlite Insulation** in walls and roofing to improve thermal performance.
- A **Low-Temperature Air-to-Water Heat Pump** by Daikin for energy-efficient heating.
- **Zehnder ComfoAir** for the efficient ventilation and conditioning of indoor air.
- **MDPE** for water management systems, promoting sustainable water practices.
### Community Integration
The design extends beyond individual residences to enhance community engagement. Features include terrace gardens for biodiversity and stormwater management, as well as shared public spaces that encourage social interaction among residents. These elements ensure that the micro-homes contribute positively to the surrounding community while maintaining a resilient urban environment.