5 key facts about this project
## Analytical Report: House of the Future
### Overview
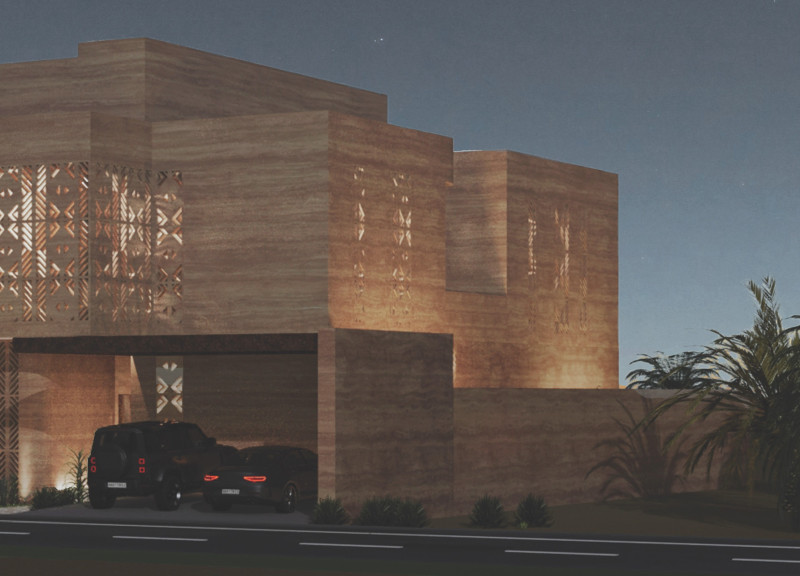
Located in the United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future exemplifies the integration of contemporary architectural practices with Emirati cultural heritage. The residence is designed to accommodate a family of four to six members, emphasizing a balance between modern functionality and traditional values. Its thoughtful design aims to provide a living environment that is both innovative and deeply rooted in the region's cultural narrative.
### Spatial Organization and Access
The dwelling encompasses a total area of 536 square meters across three levels, structured to optimize family living. The ground floor, measuring 209 square meters, features key communal spaces, while the first floor offers 268 square meters dedicated to private quarters. A 59-square-meter roof access area enhances vertical connectivity within the layout.
The massing strategy employs a combination of horizontal and vertical planes to facilitate natural light and airflow, while ensuring privacy. The design incorporates three distinct entrances, allowing for streamlined access to various functional zones: an entry for the traditional majlis, a secondary entrance leading to dining and leisure areas, and a dedicated access point for the kitchen and service areas.
### Material and Sustainability Initiatives
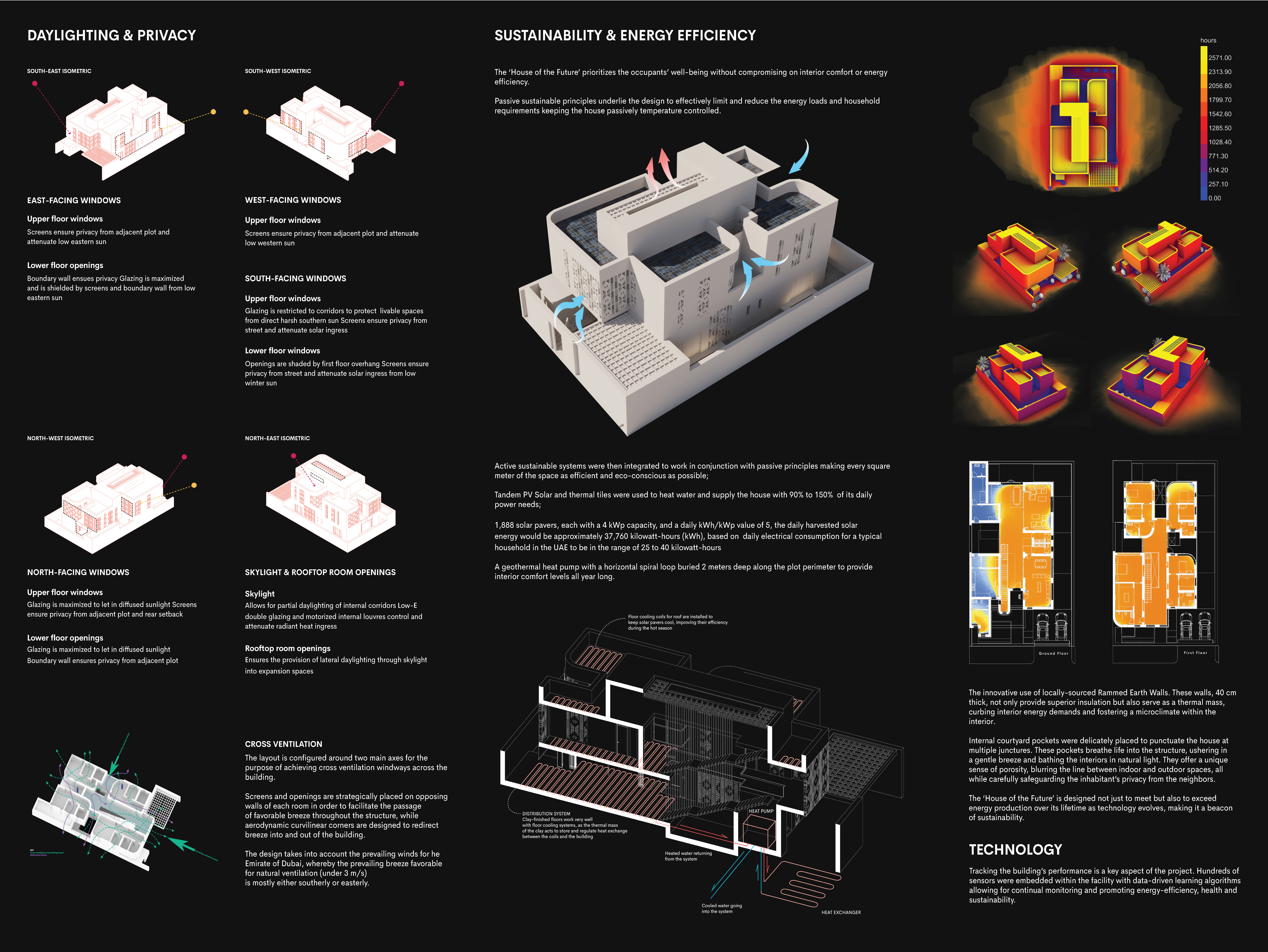
The House of the Future utilizes locally relevant materials and innovative construction techniques. Biopolymer-stabilized earth blocks serve as the primary building material, reducing reliance on conventional cement and promoting environmental sustainability. A modular system of these lightweight earth blocks enables rapid assembly without compromising structural integrity.
In terms of energy efficiency, the residence integrates solar energy systems that supply approximately 90% of its electrical needs. The design strategically employs cross-ventilation and daylighting strategies through carefully positioned windows and skylights, enhancing airflow and reducing dependence on artificial cooling. Additional features include modular screen panels that function as breathing walls, allowing both light and air to permeate the home while paying homage to traditional architectural motifs.