5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
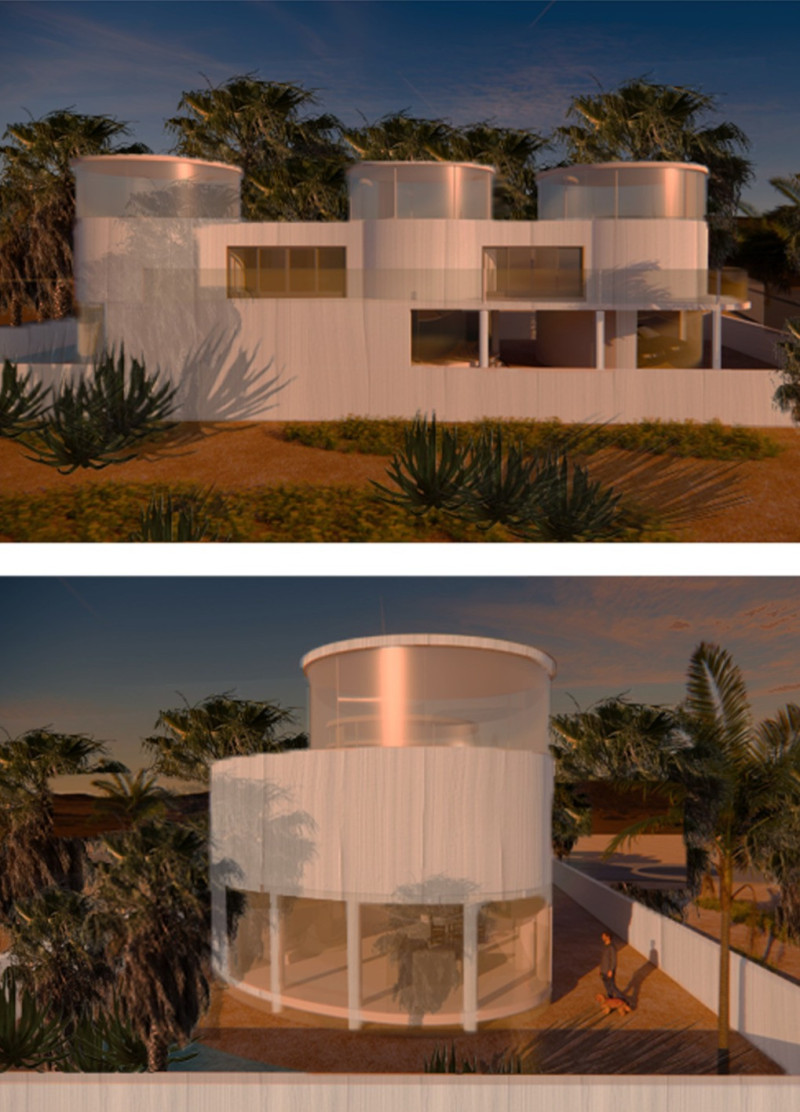
Located in the United Arab Emirates, The Salt Project addresses significant environmental challenges associated with desalination and sustainability. This residential structure employs innovative architectural solutions that leverage the region's abundant saltwater resources while promoting sustainable living practices. Designed to align with the local climate and lifestyle, the project serves as a relevant example of responsible architecture in the face of increasing brine disposal issues.
### Architectural Concept and Design Intent
The design concept explores the utilization of salt as a primary building material, specifically targeting the environmental challenges posed by seawater desalination processes. By incorporating byproducts from brine into the architectural fabric, a living environment is created that emphasizes functionality and eco-consciousness. The spatial arrangement is reminiscent of organic forms found in coral reefs, contributing to an immersive experience that enhances both aesthetics and environmental awareness.
### Form, Materiality, and Sustainability
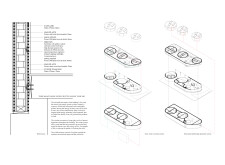
The Salt Project features three cylindrical volumes capped with domes, integrating naturally with the surrounding landscape of palm trees and desert flora. The bright, white plastered surfaces contrast with the local desert textures, reinforcing the connection between the built environment and its natural context.
Material selection has been critical to the project's design philosophy, incorporating the following elements:
- **Salt Bricks**: Enhanced with sodium carbonate and epoxy for durability against environmental factors.
- **Oriented Strand Board (OSB)**: Provides insulation and serves as a humidity barrier, ensuring structural integrity.
- **Stainless Steel**: Utilized for structural connections and features that require longevity.
- **Plaster**: Applied to both interior and exterior surfaces, promoting a cohesive aesthetic while enhancing thermal performance.
The project also includes a range of sustainable features such as integrated solar panels for renewable energy production, a greywater recycling system for irrigation, and natural ventilation strategies that allow for effective air circulation. Native landscaping surrounding the structure employs drought-resistant plants, further enhancing ecological balance and reducing irrigation needs.