5 key facts about this project
# House of the Future Project Overview
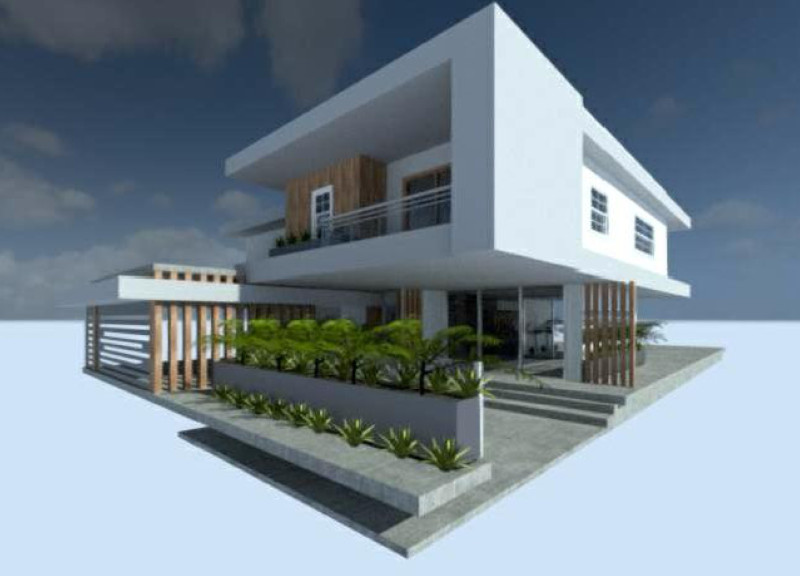
Located in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future redefines contemporary residential architecture through innovative spatial planning and sustainability principles. Intended to create a livable environment that meets the cultural context of the region, the design emphasizes adaptability and connectivity between indoor and outdoor spaces. The structure is oriented to foster both social interactions and privacy, addressing the environmental challenges unique to the desert climate of Dubai.
## Spatial Configuration
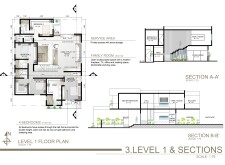
The ground floor features several distinct zones, including a living room enhanced by cross ventilation through tri-panel sliding doors, providing access to outdoor areas. The dining area, adjacent to the living space, benefits from double-height ceilings and a fireplace, balancing comfort with functionality. A strategically located kitchen ensures privacy and efficiency with direct access to a pantry. The service block accommodates essential utility spaces, while the Majlis offers a semi-open area conducive to social gatherings, emphasizing both interaction and privacy.
On the upper level, private living spaces are prioritized. The master bedroom includes an en-suite bathroom and walk-in closet, along with access to a balcony that reinforces the connection to outdoor spaces. A multifunctional family room supports various leisure activities, and four additional bedrooms, each with individual bathrooms, ensure comfort and privacy for residents and guests. The hall design promotes interaction among occupants while maintaining accessibility to all bedrooms.
## Material Choice and Environmental Strategy
Attention to material selection plays a critical role in achieving sustainability goals. The design incorporates smart glass windows to minimize heat entry while allowing natural light, enhancing energy efficiency. Concrete is utilized for its structural properties and thermal mass, while cool brick assists in maintaining a comfortable interior temperature in the desert climate. Natural wood is used in external cladding, providing aesthetic appeal while improving thermal insulation. Integrated planting systems support environmental quality and aesthetics, contributing to temperature regulation and air purification.
The design also emphasizes the use of recyclable materials and implements architectural overhangs to shield windows from excessive sunlight, promoting energy conservation throughout the year. This thoughtful approach to materiality not only supports the building's performance but also aligns with broader sustainability objectives.