5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
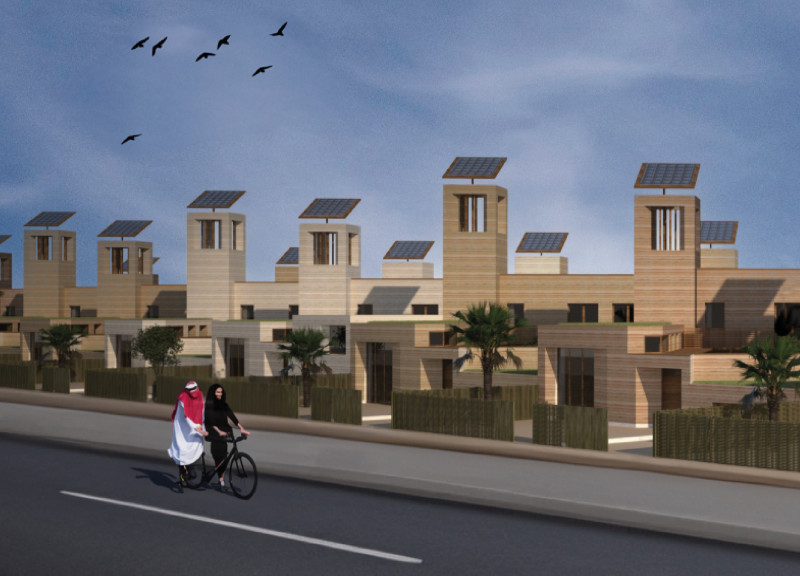
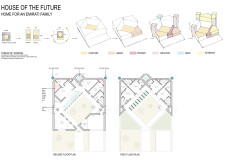
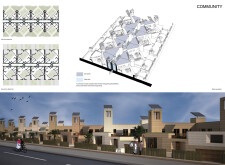
Located in the United Arab Emirates, the residence designed for an Emirati family reflects a harmonious integration of traditional architectural elements and modern sustainable practices. This design addresses ecological, social, and cultural needs by reinterpreting the historical context of Emirati courtyard houses, emphasizing the importance of community interaction and environmental responsiveness.
### Sustainability and Material Integration
The approach prioritizes sustainability through the use of local materials and innovative technologies. Key features include an integrated water management system for grey water recycling, the incorporation of solar panels for energy efficiency, and strategic layout elements that enhance cross-ventilation and natural lighting. The construction employs a diverse range of materials, such as rammed earth for thermal efficiency, concrete for structural stability, and timber for visual warmth and energy conservation. Glass elements promote connectivity with the outdoor environment, while local textiles contribute to cultural authenticity.
### Spatial Composition and Usability
Arranged over two levels, the layout progresses from communal to private spaces. The ground floor features open communal areas designed to facilitate family interaction, alongside dedicated private sections for individual rooms and technical spaces. The first floor includes bedrooms that prioritize privacy while offering scenic views, complemented by adaptable shared areas. This strategic organization promotes flow and connectivity, reflecting the cultural values of community while ensuring the safeguarding of personal space.