5 key facts about this project
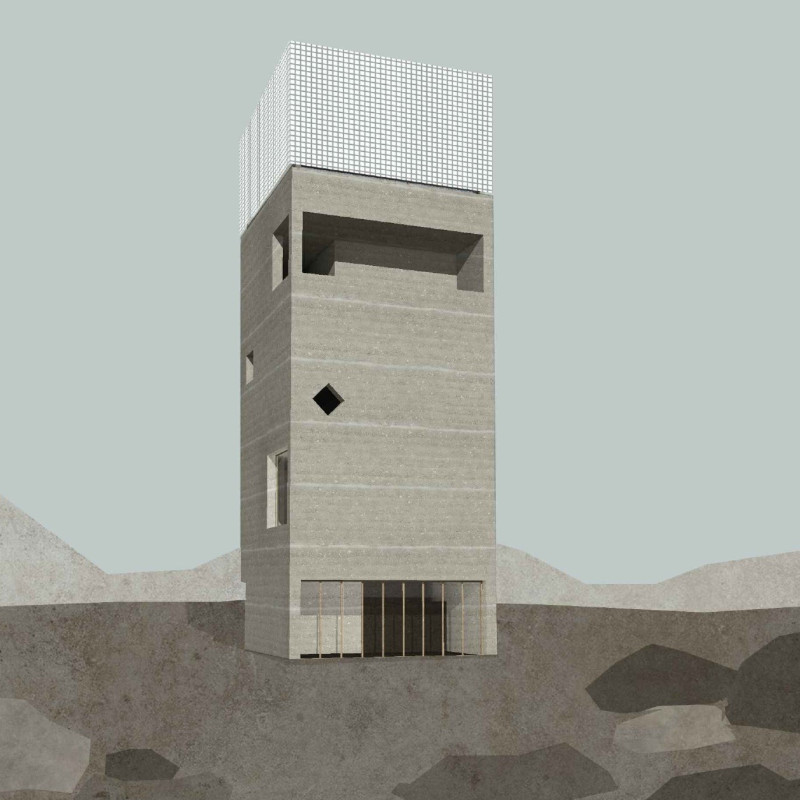
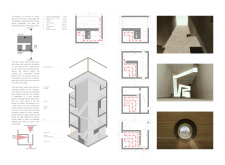
The setting near Grjótagjá's caves offers a special exploration of how natural features can blend with buildings. The design is known as a "cave tower," representing the experience of being inside a cave along with the viewpoint provided by a tower. This combination invites visitors to engage with both the environment and the structure.
Conceptual Framework
The observation tower is crafted to fit into the surrounding rocky landscape effectively. It serves as more than just a place for viewing; it makes a statement about the relationship between built forms and nature. Rather than tapering upwards like many traditional towers, the interior space expands as one climbs, allowing more light in and creating a feeling of openness.
Entrance and Visitor Engagement
Entering the tower, visitors walk through an opening designed like a crevice in stone. This leads to a visitor center featuring an information stand. This element connects visitors with different experiences: the caves, the observation area, and a waiting space. Such a design clarifies the path and makes it easier for guests to navigate their experience.
Interior Atmosphere and Experience
Inside, the design creates a cave-like feel through carefully shaped elements. Curved stairs guide visitors along a pathway, presenting different heights and spaces that interact visually. A café located on an upper level offers views of the surrounding area, allowing a moment of reflection on the landscape beyond the tower.
Spatial Dynamics and Materiality
The structure includes voids that enhance the experience by framing views of the landscape as visitors move about. The use of rammed earth in construction adds a practical and attractive quality, aligning with goals for sustainability. Additionally, aluminum components are employed for their lightweight and cost-effective properties, contributing to the tower's visual design while addressing local weather conditions.
A modular walking path system, designed in a 1x1 meter configuration, is flexible for various terrains. This adaptability allows for easy movement across both flat ground and slopes, making connections to the caves or the fissure created by the shifting continental plates.
To support environmental sustainability, the roof design incorporates a system for collecting rainwater, enhancing drainage efficiency and integrating nature into the overall architectural plan of the tower.