5 key facts about this project
## Overview
This architectural design project is located in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and is focused on sustainable modular living within the context of urban planning. The intent is to create a resilient urban environment that addresses both the building and landscape scales, aiming to facilitate adaptive responses to the challenges presented by rapid urbanization.
## Urban Planning Concepts
### Future Urban Hubs
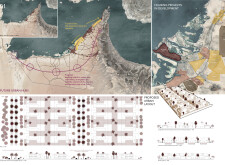
The proposal articulates a vision for future urban hubs that develop inland, countering the typical shoreline expansion prevalent in the region. It aims to enhance mobility networks and establish new centers that address urbanization challenges through a carefully considered spatial arrangement. The urban layout incorporates protective green buffers to mitigate environmental impacts while promoting social interaction and functional living spaces.
## Materiality
### Unique Material Selection
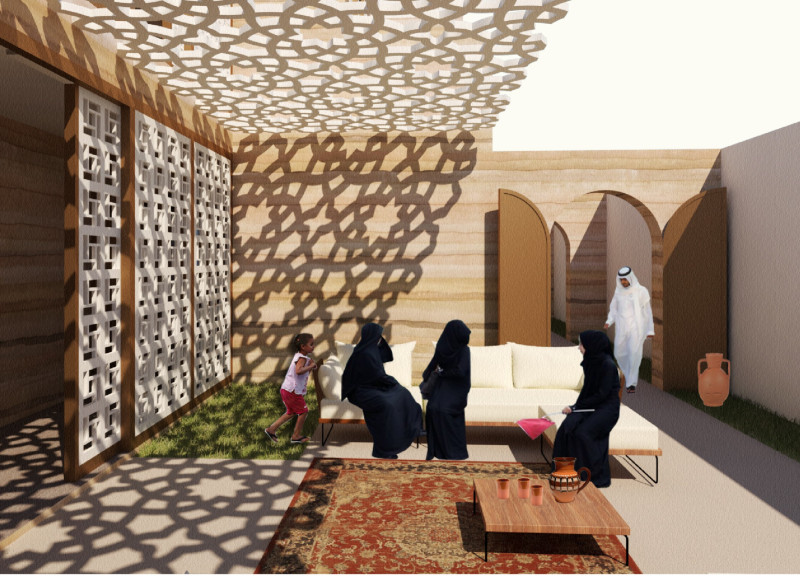
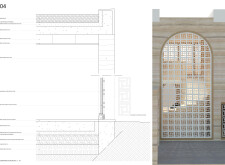
Key materials selected for construction include rammed earth, which minimizes ecological impact and draws from the region's historical building traditions, and concrete, which provides structural durability. Wood elements add warmth, while glass treatments ensure natural light and energy efficiency. Decorative grilles, inspired by traditional motifs, integrate modern design with cultural references, enhancing ventilation and visual interest. The emphasis on rammed earth distinguishes this project within contemporary architectural practices, promoting sustainability and ecological harmony.
## Design Outcomes
### Interior and Exterior Spaces
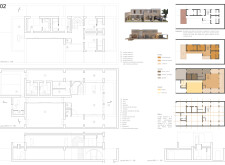
The design strategically incorporates multiple courtyards to foster natural airflow and create a temperate internal climate. These outdoor spaces are intended for social interaction, while the flexible interior layout accommodates changing family dynamics, with provisions for future use of spaces, such as the rooftop. The clear division between private family areas and public guest zones respects local social and cultural practices, enhancing the overall hospitality within the dwelling.
### Sustainability and Environment
Sustainability is paramount in this project, evidenced by the integration of landscape architecture, water management strategies, and the use of ecological materials. The design not only respects the region's heritage but also interprets modern needs through environmentally conscious methods, presenting a balanced approach to contemporary urban living.
## Visual Elements and Functionality
### Structural and Aesthetic Details
The facades combine solid rammed earth with transparent glass, creating a visually dynamic interplay of light and shadows within the interior spaces. The innovative floor plan allows for both communal and private experiences, ensuring accessibility and engagement in shared areas such as living and dining rooms. Additionally, the integration of gardens and pools promotes outdoor living, aligning with the UAE's climate and lifestyle while enhancing leisure activities within daily life.