5 key facts about this project
**Overview**
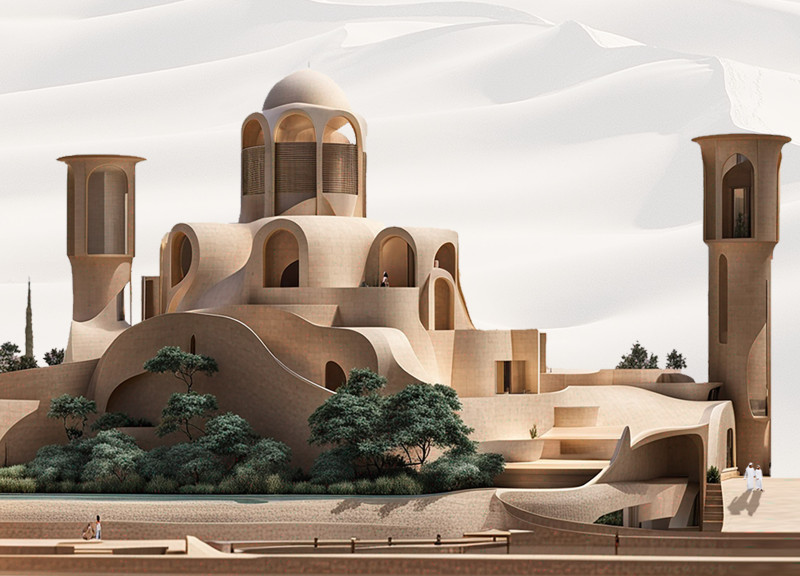
Located in Dubai, the House of the Future embodies a synthesis of traditional Islamic architectural elements and contemporary sustainable technologies. This residential design is informed by the rich cultural heritage of the United Arab Emirates, aiming to foster a sense of place while addressing the needs of modern living. Its conceptual framework emphasizes multi-generational living and encourages social interaction through its communal spaces, reflecting key aspects of Emirati culture.
**Architectural Identity and Materiality**
The architectural design features fluid forms interspersed with domes, arches, and intricate geometric patterns, drawing inspiration from traditional motifs while introducing modern aesthetics. The facade employs soft, warm desert tones, promoting an integration with the surrounding environment. Sustainable materials are prioritized to uphold both ecological and aesthetic standards. Natural light is harnessed through the strategic placement of skylights and clerestories, significantly reducing reliance on artificial lighting. Passive solar techniques contribute to an inviting interior atmosphere, ensuring comfort throughout the year.
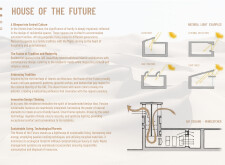
**Sustainable Engineering Practices**
Innovative air-flow systems, including windcatchers and cross-ventilation strategies, enhance indoor climate control while minimizing mechanical dependency. In addition, the design incorporates advanced resource management systems focused on waste reduction and water recycling, aligning with eco-friendly practices. Solar panels and energy-efficient technologies further illustrate the commitment to sustainability, establishing the project as a forward-thinking residential model in a rapidly urbanizing context. The integration of communal spaces, particularly the Majlis, reflects the values of family and hospitality central to Emirati culture, enhancing both social cohesion and the user experience.
**Materials Specification**
The construction utilizes sustainable local stone, rammed earth, and adobe for the exterior, coupled with lightweight reflective roofing systems to improve energy efficiency. High-efficiency, double-glazed glass is employed for windows, while interior finishes consist of natural woods, sustainable composites for flooring, and organic textiles, reinforcing the project's ecological and cultural considerations.