5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
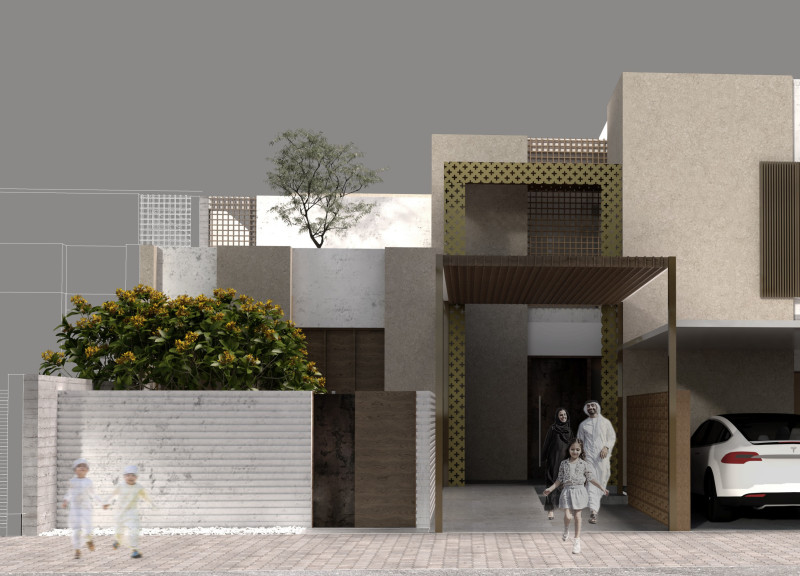
Located in an urban environment, the Courtyard House aims to blend contemporary living with traditional design principles, emphasizing both community engagement and individual family needs. The intent of the design is to create a modern living space that fosters interaction among residents while reflecting regional cultural heritage. The project prioritizes sustainability, providing a luxurious yet functional dwelling tailored for evolving family dynamics.
### Spatial Configuration and Flexibility
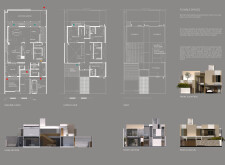
Central to the design is an innovative interpretation of the traditional courtyard, which serves as both a private retreat and a space for communal activities. The layout encourages natural light and vegetation, enhancing family well-being and promoting outdoor engagement. The interior spaces are designed with flexibility in mind, allowing areas such as the dining room to adapt for different uses, accommodating a variety of family activities and gatherings.
### Materiality and Environmental Integration
The selection of materials for the Courtyard House underscores both ecological responsibility and local cultural relevance. Key materials include precast rammed earth for its thermal efficiency and low environmental impact, as well as steel-concrete composite systems that optimize construction processes. Additional elements, such as prefabricated bathroom modules and waterproof roofing panels, further enhance durability and sustainability. Incorporating photovoltaic panels facilitates energy generation, while decorative mashrabiya screens offer passive cooling and aesthetic value, echoing traditional architectural themes while promoting privacy.
The design also incorporates systems for rainwater collection and natural ventilation, effectively minimizing the building's carbon footprint and reinforcing its environmental commitment. Pathways and communal gardens are strategically integrated to promote social interaction among residents, thus fostering a sense of community within the architectural framework.