5 key facts about this project
**Dar Al Sahra Overview**
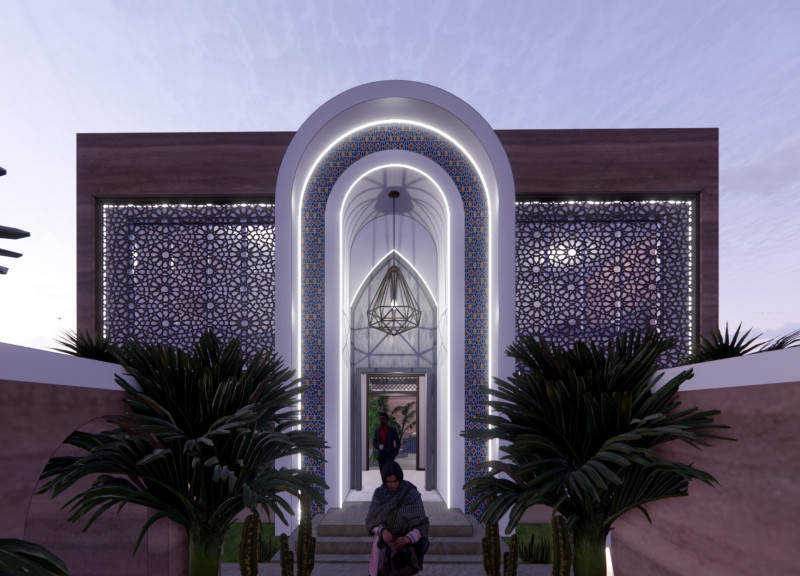
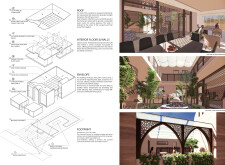
Located in the Middle East, Dar Al Sahra integrates traditional Emirati architectural concepts with contemporary sustainable practices. The design seeks to address environmental challenges within the region and promotes a lifestyle that reflects the rich cultural heritage of the Middle East. Central to the design is a courtyard layout that emphasizes social interaction while maintaining private family spaces, fostering community connections.
**Cultural and Environmental Integration**
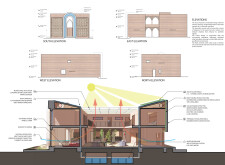
The architectural language is deeply rooted in local traditions, characterized by elements such as prominent arches and decorative screens that serve both aesthetic and functional roles. The incorporation of sustainability strategies is a key aspect of this project. Solar panels on the roof harness the region's abundant sunlight, while a rainwater harvesting system effectively gathers roof runoff for irrigation and household use. Natural ventilation is achieved through strategically placed openings, enhancing comfort without excessive reliance on mechanical cooling systems. The use of locally sourced materials, including rammed earth, minimizes transportation emissions, supports the local economy, and provides essential thermal mass, further promoting energy efficiency.
**Material Choices and Functionality**
The material selection within Dar Al Sahra emphasizes both performance and visual appeal. Rammed earth contributes to natural insulation and a warm ambiance, while structural insulated wall panels enhance energy efficiency. Wood elements serve dual purposes by adding aesthetic value and functional shading. Additionally, high-performance glass is used in windows to optimize natural light while reducing solar gain. The overall design achieves a harmonious interplay between interior and exterior spaces, with features such as a central courtyard promoting community engagement and a versatile layout accommodating various family needs. The integration of native landscaping enriches the ecological habitat surrounding the structure, enhancing biodiversity and ensuring compatibility with the natural environment.