5 key facts about this project
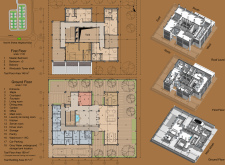
## Overview
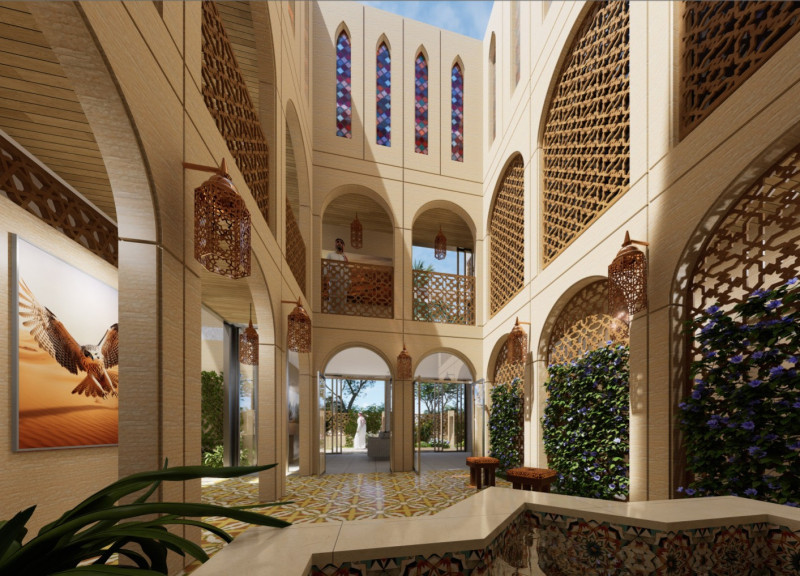
Located in the Nad Al Sheba neighborhood of Dubai, the Dubai Habitat project exemplifies a commitment to sustainable living and cultural integration within the context of contemporary architecture. The design promotes innovative technology while honoring traditional Middle Eastern architectural elements, aiming to create a community-oriented environment that addresses the specific challenges of urban dwelling in arid climates.
## Spatial Strategy and Community Interaction
Adaptive living spaces define the project’s spatial organization, which features interconnected layouts designed to enhance openness and facilitate airflow. The integration of voids throughout the structure not only encourages natural light but also improves climatic comfort. Traditional elements such as windcatchers and courtyards are incorporated to leverage passive cooling techniques and foster social connectivity among residents. These features are complemented by modular housing configurations that allow for customization, thereby accommodating diverse family sizes while reinforcing communal living.
## Material Selection and Sustainability
The selection of materials reflects both sustainability and aesthetic considerations. Iroko wood, noted for its durability, forms essential structural and decorative elements. White precast concrete provides structural integrity along with energy efficiency through thermal massing. Rammed earth concrete enhances thermal performance and aligns with local vernacular architecture principles. Additional sustainable features include brown roofs and vegetable gardens that promote biodiversity and insulation benefits, while mashrabiyya screens offer privacy and enhance ventilation in a desert environment. Energy generation is supported by solar panels, including an innovative spherical sun power generator, and a vortex bladeless turbine, which provides environmentally friendly energy solutions with lower maintenance requirements.