5 key facts about this project
### Overview
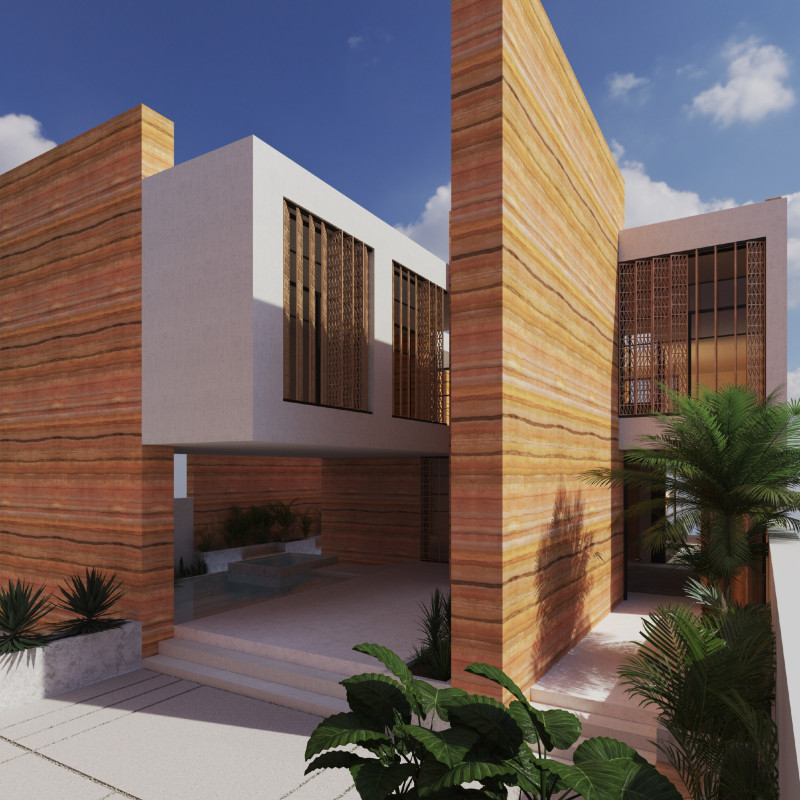
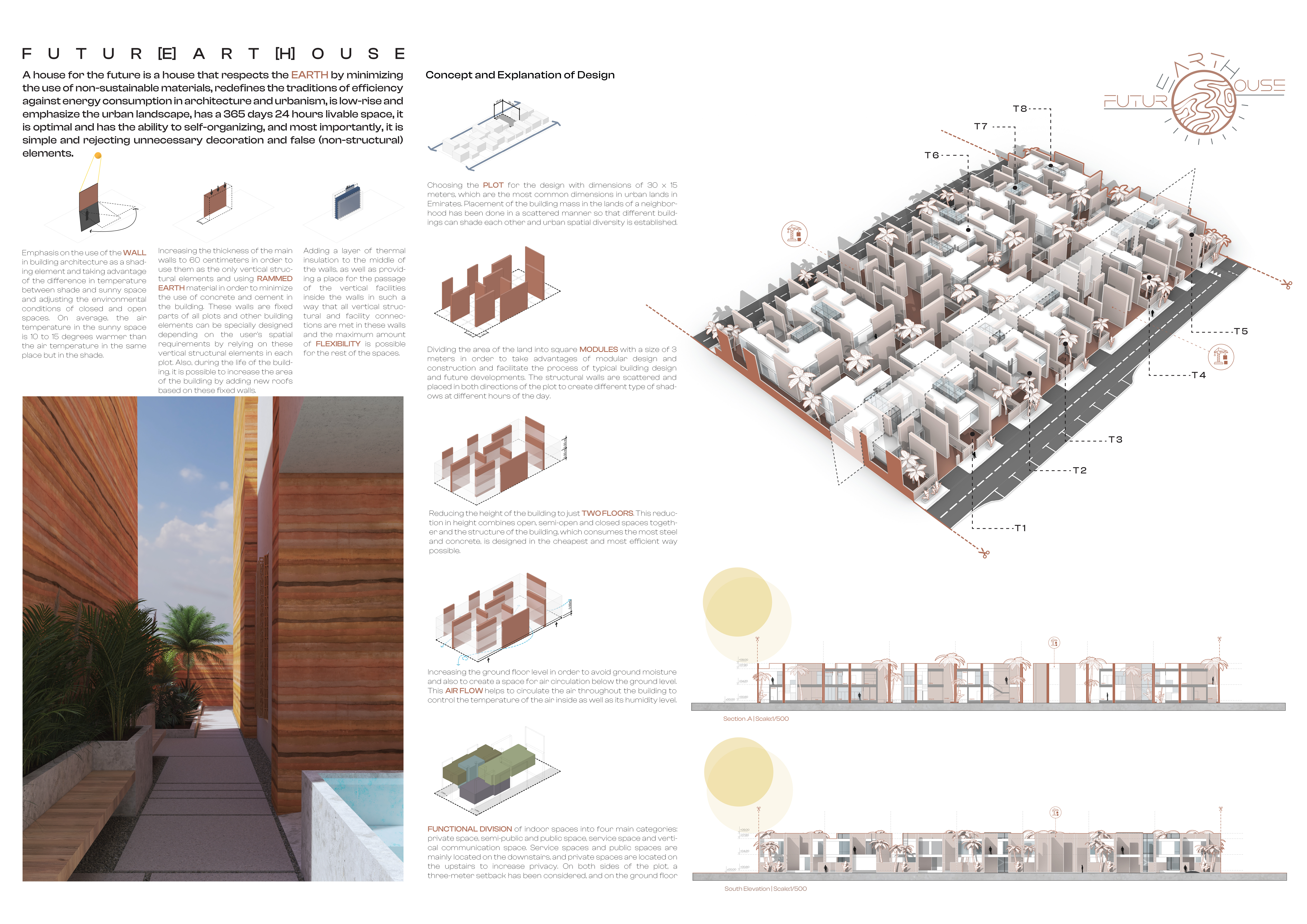
The Future Earth House is located in an urban setting, designed with a focus on sustainability and efficient use of space. It aims to address environmental challenges by minimizing the use of non-sustainable materials while providing a flexible living environment for future residents. The project emphasizes self-organization and simplicity, moving away from ornate decorative elements to create a space that harmonizes with its surroundings.
### Spatial Strategy and Community Integration
The design features an open-plan layout that promotes connectivity and facilitates natural airflow and light. The ground floor includes shared communal areas such as gardens and pools, enhancing social interaction among residents. Modular configurations allow for adaptability, catering to individual preferences while maintaining a sense of community. The arrangement of units not only ensures privacy but also encourages accessibility to communal amenities, balancing personal space with shared experiences.
### Materiality and Construction Techniques
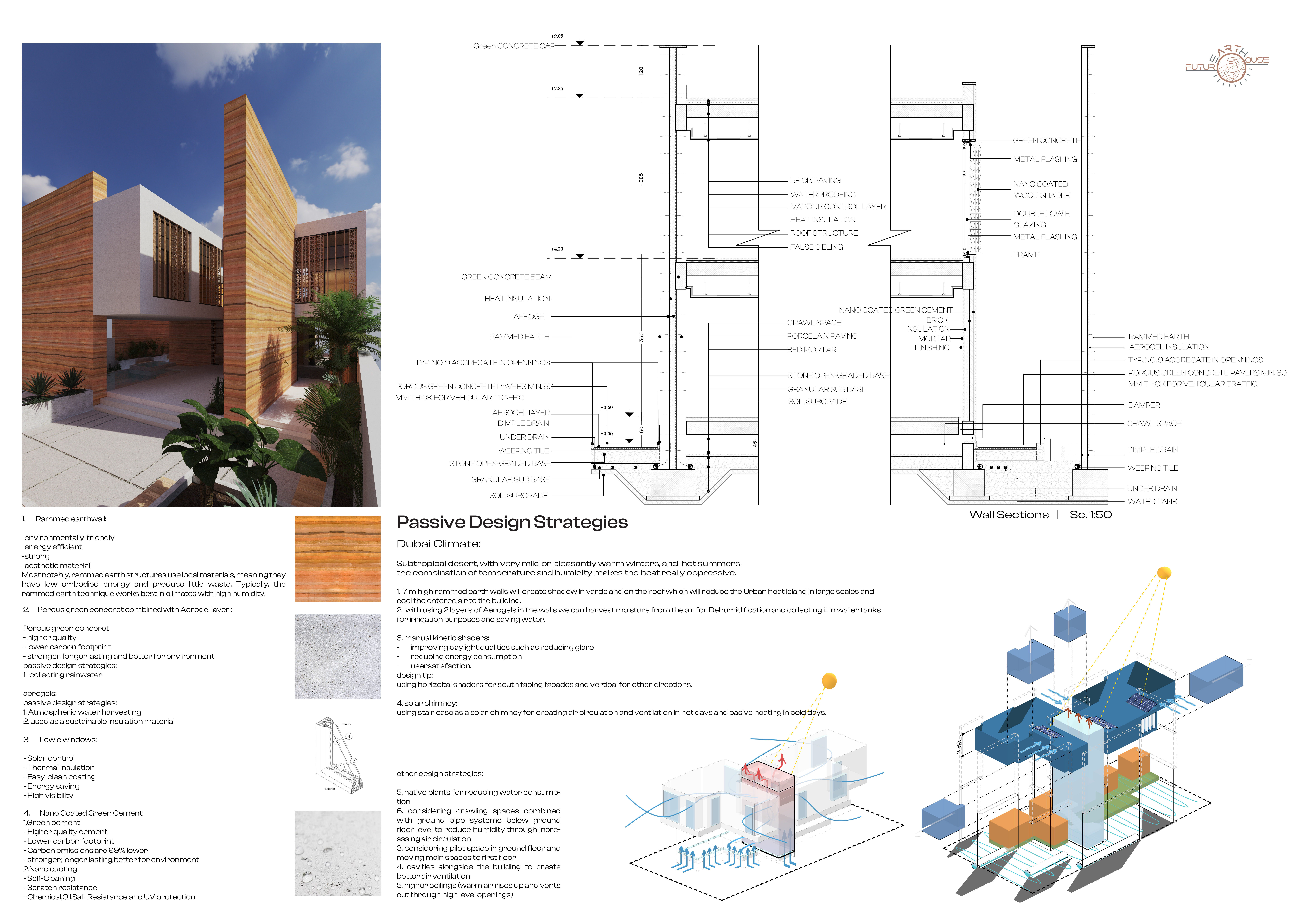
A careful selection of materials underpins the design's commitment to sustainability. Rammed earth serves as the primary building material, leveraging its thermal mass to regulate indoor temperatures. Porous green concrete enhances drainage and reduces environmental impact, while local natural stone adds durability and aesthetic value. Glass is strategically incorporated for natural lighting and passive solar heating, while sustainably sourced wood contributes warmth and texture to the interiors. These material choices reflect a broader intention to minimize ecological footprints, aligning with the project's ecological goals.
### Passive Design Strategies
In response to the subtropical climate, the Future Earth House employs passive design strategies to optimize energy efficiency. Strategic orientation and shading devices mitigate direct sunlight exposure, thereby reducing cooling needs. High ceilings and operable windows facilitate natural ventilation, promoting thermal comfort. Innovations such as solar chimneys enhance air exchange, contributing to overall climate control within the structure. The integration of these elements illustrates a comprehensive approach to environmental responsibility in urban housing design.