5 key facts about this project
### Overview
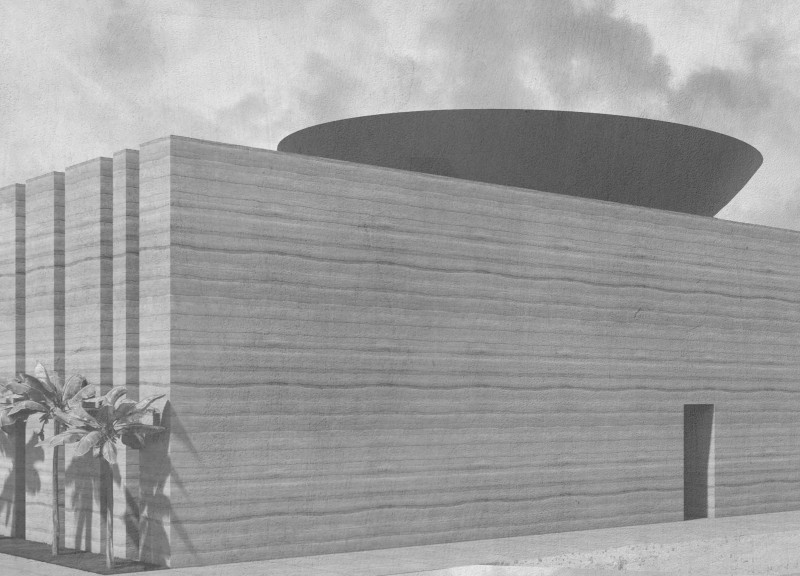
Located in Dubai, the Temple House design proposal emphasizes the importance of water, a vital resource in the region's arid climate. This project aims to integrate sustainable practices while remaining attuned to traditional Emirati architectural elements, creating a space that fosters both communal interaction and individual privacy.
### Spatial Organization
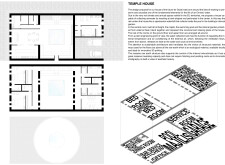
The layout of Temple House is structured around an open central atrium, known as the mishrab, which serves as the focal point of interaction for occupants. The ground floor features two wings containing functional spaces, including bedrooms and a kitchen, allowing for efficient airflow and the penetration of natural light. The upper floor accommodates additional bedrooms, providing seclusion for residents while maintaining a connection to the central communal area.
### Material Selection
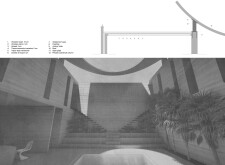
The construction materials selected for Temple House align with local environmental conditions and sustainability goals. Locally sourced raw earth enhances thermal insulation, reducing energy dependency. Wood is used for structural elements, offering warmth and texture, while steel and water-resistant materials are incorporated to ensure durability against the region's climatic challenges. Furthermore, an innovative water collection system channels rainwater into a central reservoir in the atrium, enhancing cooling through evaporation while offering a visually calming feature.
The design reflects a balance between traditional and contemporary architectural elements, with minimalistic aesthetics that emphasize natural materials. Large walls of raw earth are complemented by wooden details, creating a harmonious interior environment enriched by natural light. These choices contribute to a sustainable living experience, underscoring the importance of harmony between architecture and nature.