5 key facts about this project
### Overview
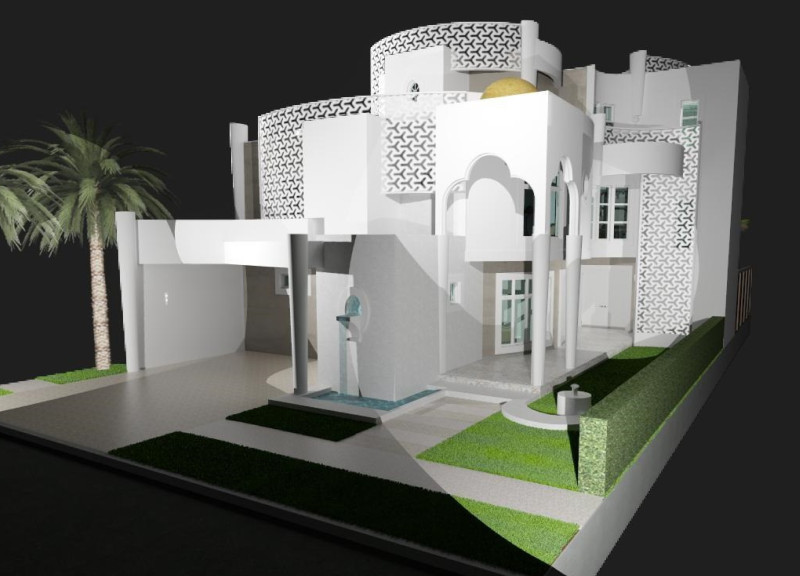
The "House of the Future" is located in a contemporary urban setting in the UAE, designed to reflect both modern architectural practices and Emirati cultural aesthetics. This multi-level dwelling prioritizes functionality, cultural significance, and sustainable design strategies. The project examines a unique conceptual framework, emphasizing its commitment to creating an environment that enhances family life and community interactions.
### Spatial Organization
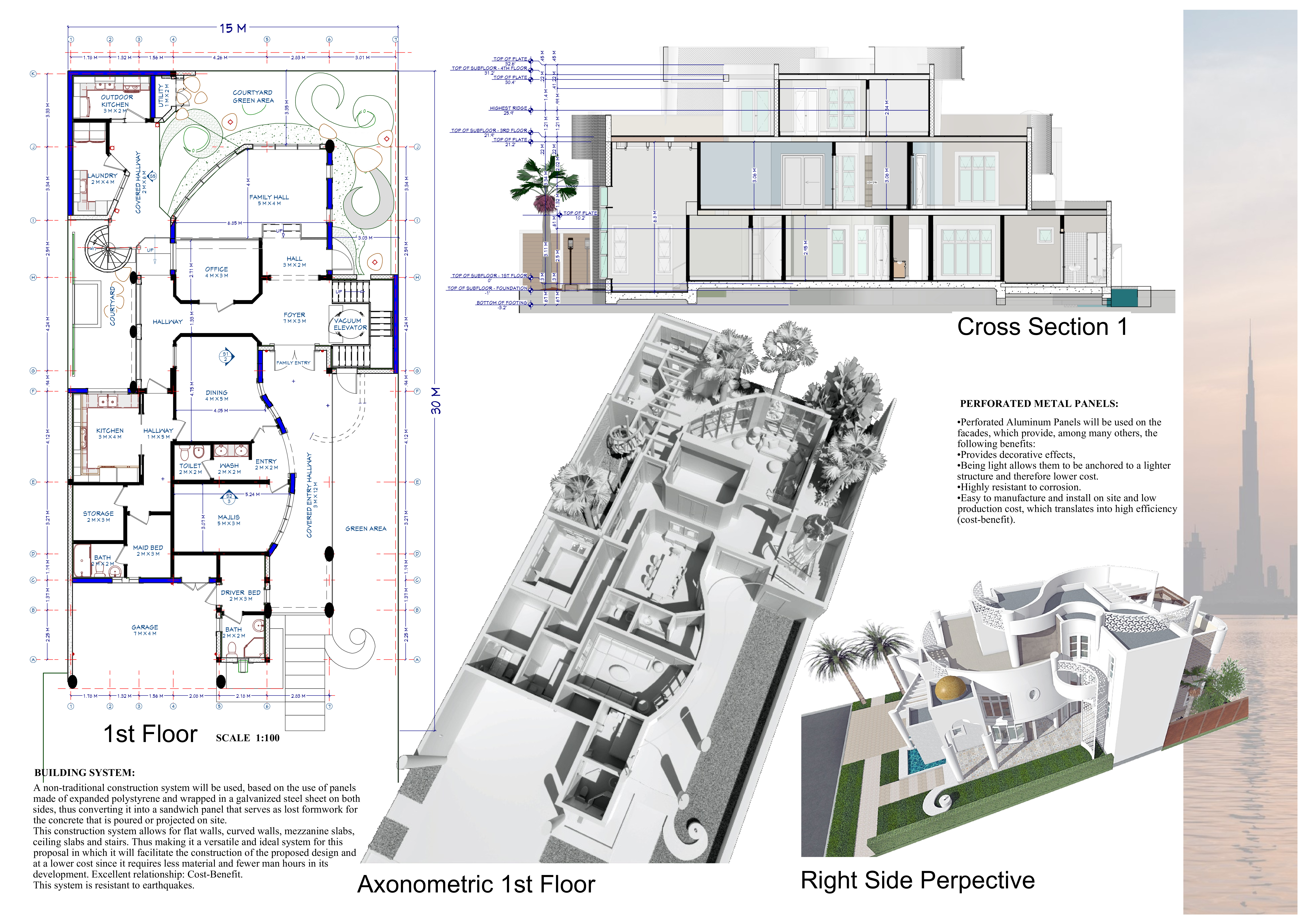
The dwelling is organized across three levels to maximize both private and communal areas while maintaining interconnectivity.
- **Ground Level**: This floor includes essential communal spaces, such as the kitchen, dining area, and family rooms, designed to promote interaction while ensuring privacy through thoughtful spatial arrangements. A central spiral staircase acts as both a functional and visual connector between levels.
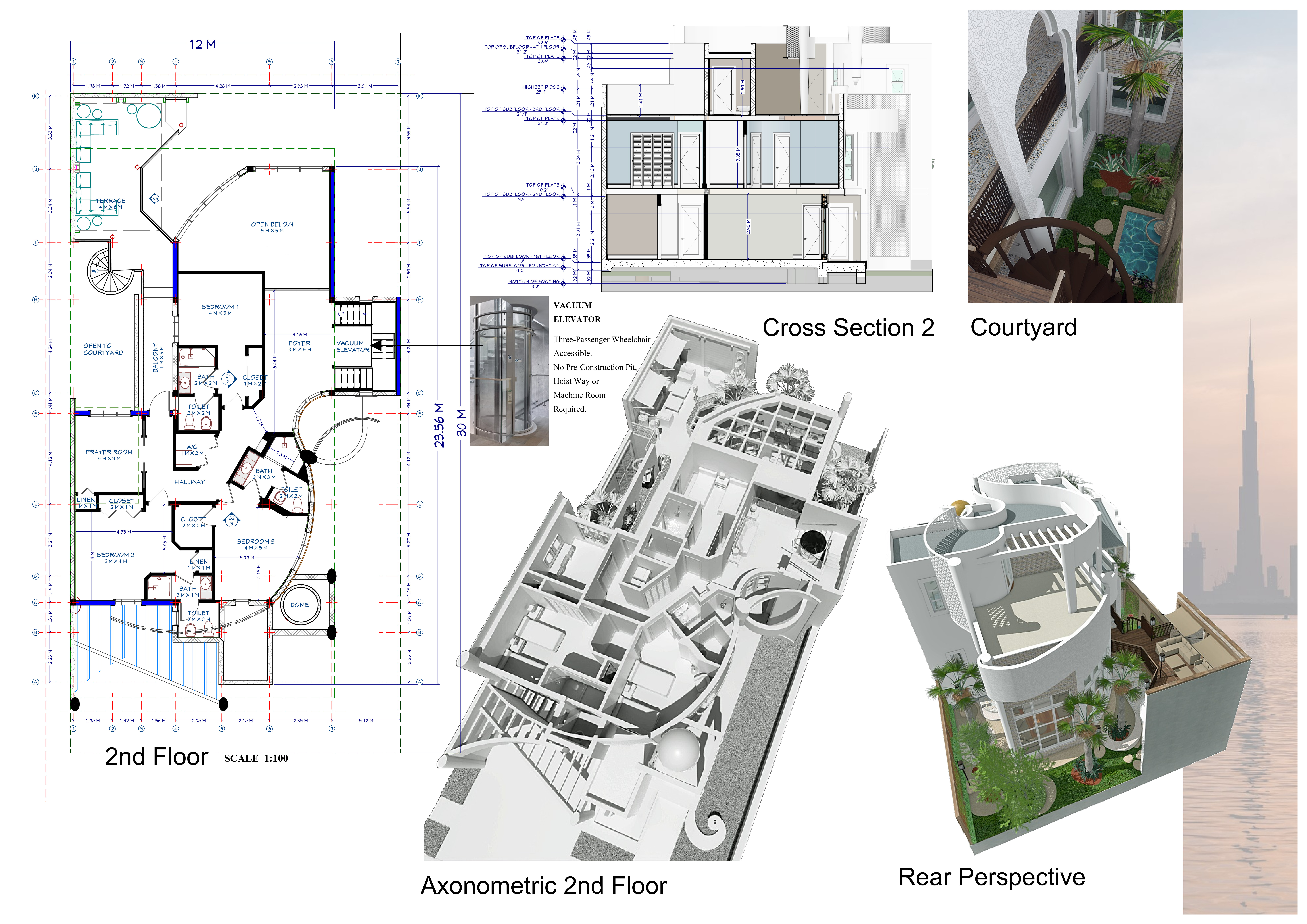
- **First Floor**: This level features private quarters, including bedrooms and an office, with extensive glazing that invites natural light, fostering a bright, inviting atmosphere and minimizing reliance on artificial lighting.
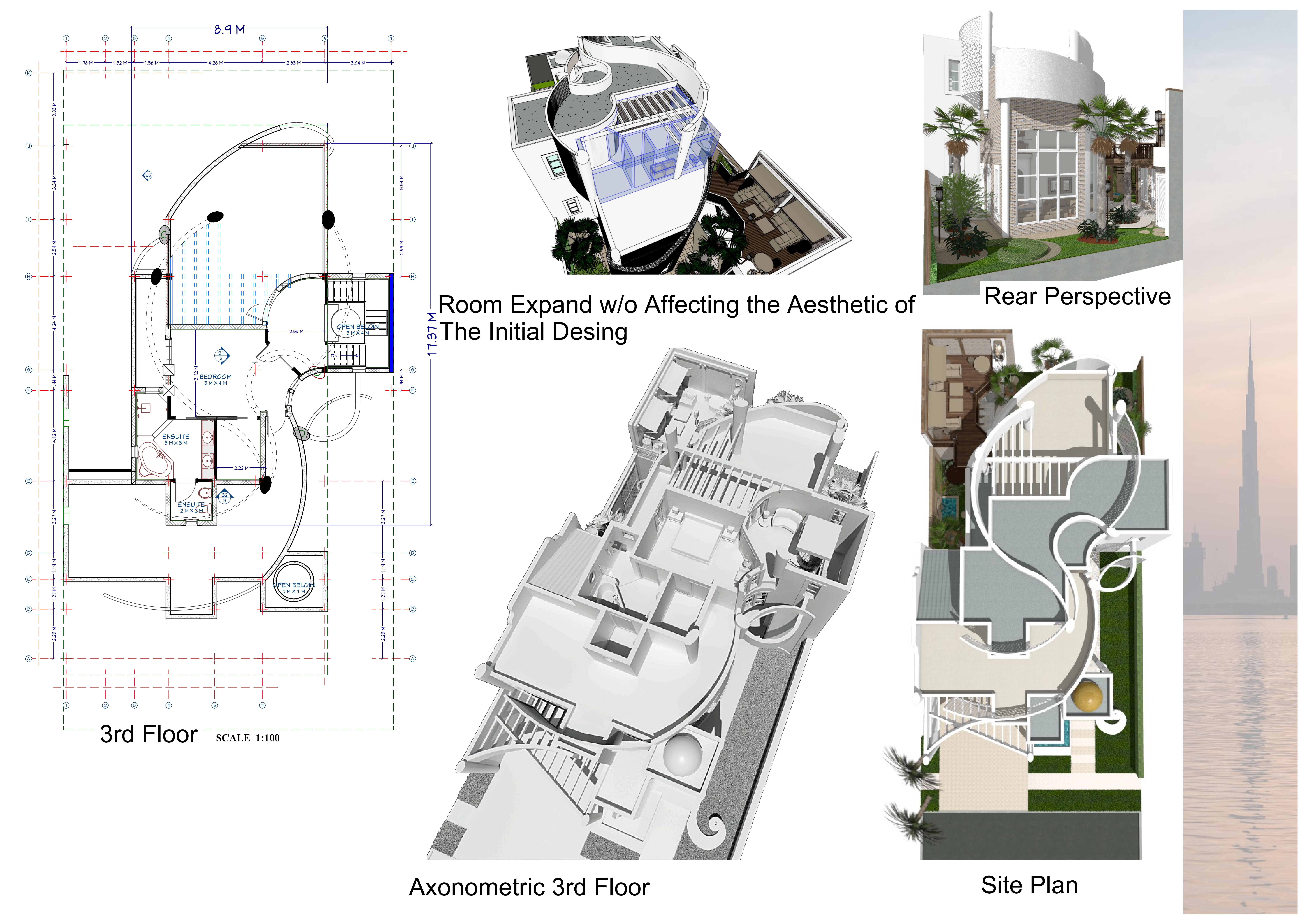
- **Upper Levels**: The second and third floors are adaptable, allowing for versatile uses such as guest suites, recreational zones, or private retreats. Accessibility is enhanced through the inclusion of a vacuum elevator, facilitating ease of movement across generations.
### Material Selection and Integration
The material palette for the residence merges traditional and contemporary elements to create a durable yet aesthetically pleasing structure.
- **Perforated Aluminum Panels**: These elements adorn the façade, offering a lightweight, decorative façade that enhances the building's visual appeal while mitigating structural load. Their corrosion resistance and ease of installation contribute to cost-effectiveness.
- **Expanded Polystyrene**: This insulation material is integrated within a galvanized steel framework, providing effective thermal management and structural integrity.
- **Glass**: The strategic use of expansive glazing enhances the relationship between indoor and outdoor environments, promoting natural light and an open feel.
- **Natural Stone and Tiles**: Incorporating traditional materials, these finishes establish a strong connection to Emirati heritage while delivering timeless elegance.
### Architectural Features
Several defining architectural elements contribute to the home's overall character.
- **Courtyards**: Numerous courtyards facilitate natural ventilation and light penetration, reinforcing connections to the outdoors and incorporating greenery that promotes tranquility.
- **Curvilinear Forms and Cultural Motifs**: The design employs smooth, flowing lines that add an organic quality, contrasting with conventional rigid forms. Intricate surface designs draw inspiration from traditional Emirati arts, skillfully blending historical references with modern expression.
This project exemplifies a carefully considered approach to contemporary residential design, balancing functional requirements with a profound connection to cultural roots and aspirations for the future.