5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
Bayt al-Wahat, located in the United Arab Emirates, is a residential structure designed to respond to the challenges of the desert environment through a focus on sustainable practices. The design integrates traditional architectural elements with contemporary methods, creating a dwelling that acknowledges its cultural and geological context. The intent is to offer a comfortable living space that minimizes ecological impact while maintaining a strong connection to the surrounding landscape.
### Spatial Organization and Functionality
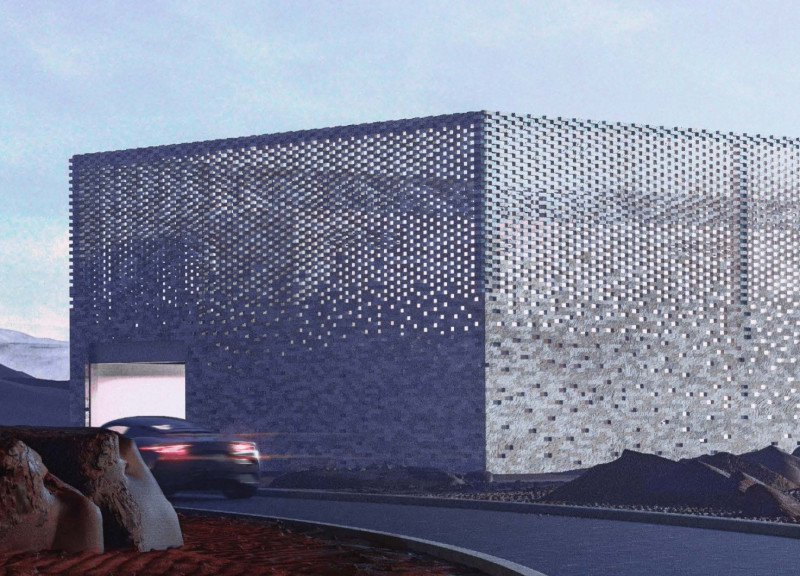
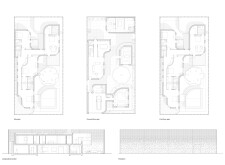
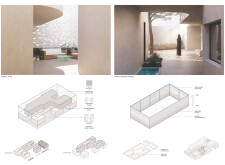
The building's form features a distinctive perforated facade constructed from local clay bricks, which not only provides aesthetic warmth but also facilitates temperature regulation through light diffusion. The layout strategically positions communal areas—such as the kitchen, dining, and living spaces—on the ground floor, while private quarters are situated upstairs. A central courtyard plays a critical role in enhancing airflow and natural light, establishing it as a focal point for both the interior and exterior spaces. The open-plan design on the ground floor encourages social interaction and allows for flexible adaptation of spaces over time, accommodating future expansions or changes in use.
### Sustainable Material Use and Design Strategies
The project's commitment to sustainability is reflected in its choice of materials and design strategies. The use of local clay bricks contributes to thermal mass, while recycled concrete minimizes the carbon footprint. Triple-glazed windows enhance energy efficiency by providing insulation, and natural stones used for flooring create a seamless connection between interior and exterior environments. The landscaping incorporates native plants that promote biodiversity and require less maintenance, and water features such as evaporation ponds contribute to cooling in the courtyard. Passive design elements, such as shaded areas and overhanging volumes, along with the integration of photovoltaic panels, are employed to reduce the need for mechanical cooling and encourage renewable energy use.