5 key facts about this project
### Overview
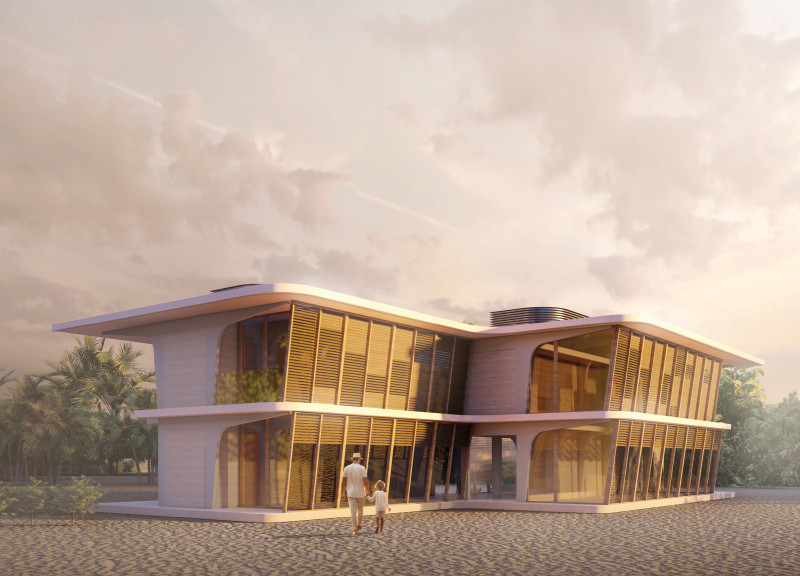
The Baggala House, designed in 2023, integrates traditional vernacular architecture with contemporary practices, aimed at addressing environmental concerns and the evolving social dynamics of family life. Located in a culturally rich context, the design reflects a commitment to sustainable living while incorporating innovative building strategies that resonate with local architectural heritage.
### Spatial Strategy and Cultural Relevance
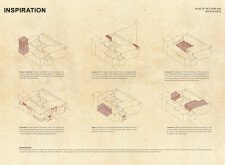
The design employs a deliberate spatial organization that fosters community interaction and personal privacy. Key features include natural ventilation systems augmented by a wind tower, which enhances indoor air quality, and a central courtyard that serves as a communal space for family and guests. The inclusion of Musharabiah elements allows for both privacy and effective cooling, in line with regional architectural traditions. The Majlis serves as a welcoming gathering area near the entrance, emphasizing its role in social interactions. This thoughtful arrangement of spaces cultivates a harmonious living environment tailored to the needs of its occupants.
### Material Selection and Environmental Responsibility
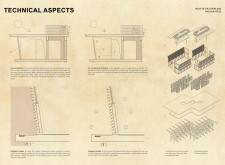
The material palette for the Baggala House emphasizes sustainability while reflecting local building practices. Prefabricated concrete modules reduce the ground footprint and allow for efficient construction. On-site poured concrete ensures durability, while earth walls employ local materials to enhance thermal performance. Advanced glazing in the intelligent facades optimizes light and temperature regulation. The use of wood for interior finishes enriches the aesthetic, providing warmth and a tactile quality. This combination of materials not only supports ecological principles but also creates an environment that respects and integrates with the surrounding landscape.
### Technical Innovations
Innovative technical systems augment the performance of the Baggala House. Natural and mechanical ventilation strategies are implemented to improve indoor air quality while allowing for the potential integration of modern air conditioning systems. Water management systems are designed to channel excess moisture from the façade, facilitating collection and reuse. The interplay between the exterior facade and indoor climate is optimized through controlled shading and ventilation, ensuring year-round comfort. Overall, these systems reflect a commitment to harmonizing technological advancements with sustainable practices.