5 key facts about this project
**Overview**
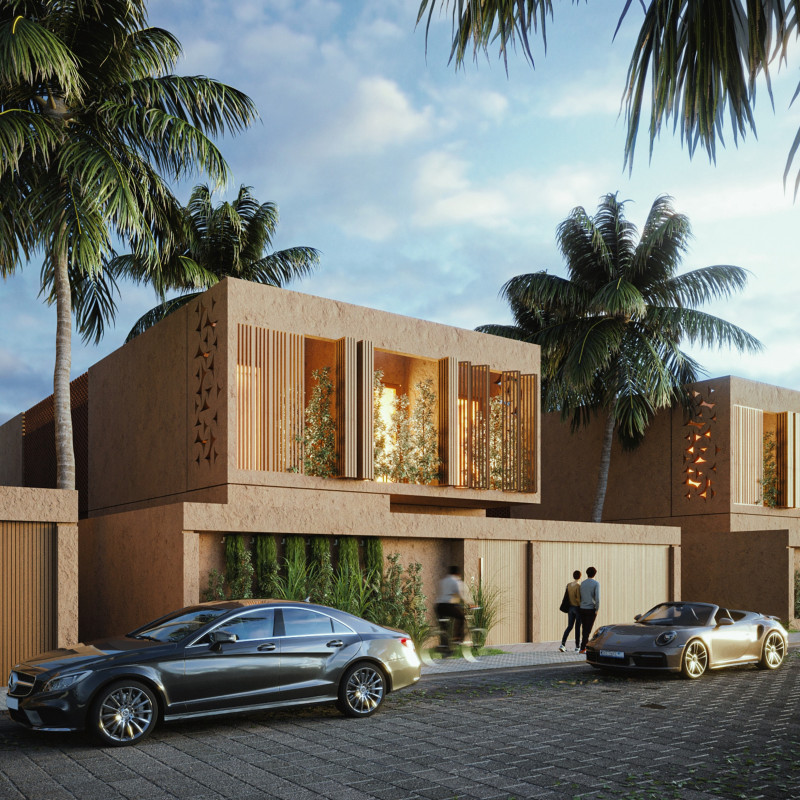
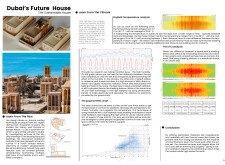
Located in Dubai, the Future House integrates sustainable design principles to address the challenges posed by the region's extreme heat and humidity. Drawing insights from traditional architectural practices of the coastal Iranian city of Bandar Abbas, the design incorporates passive strategies that minimize environmental impact while ensuring comfort and livability. This approach is characterized by features such as windcatchers and shaded terraces, which effectively engage with the landscape.
**Climate-Responsive Design**
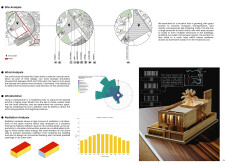
To respond to the local climate, the design employs several key strategies. A comprehensive wind analysis informs the placement of openings and windcatchers, optimizing natural ventilation throughout the living spaces. Shading devices are strategically positioned to mitigate direct sunlight exposure, effectively reducing indoor temperatures and decreasing reliance on mechanical cooling systems. The thoughtful organization of public and private zones, alongside a central courtyard, facilitates airflow and enhances outdoor leisure opportunities, contributing to overall comfort.
**Material Selection for Sustainability**
The choice of materials underscores the project's commitment to sustainability. Rammed earth serves as the primary structural element, presenting a lower carbon footprint than traditional concrete. Adjustable timber slatted shutters offer flexibility for light control and privacy, while breezeblocks create perforated walls that promote natural ventilation. The inclusion of photovoltaic panels on the roof harnesses solar energy, reducing dependency on external electricity sources. Light-colored facades reflect sunlight, minimizing heat absorption and contributing to thermal comfort within the interior spaces.