5 key facts about this project
### Overview
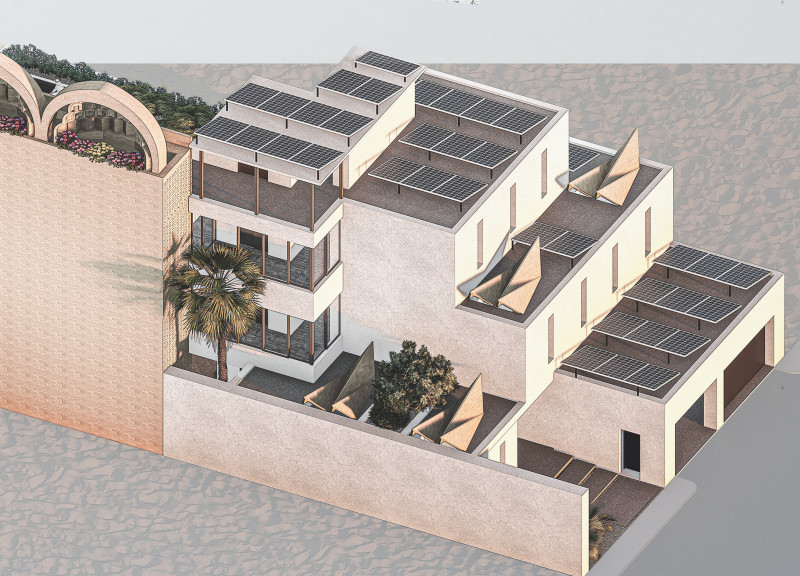
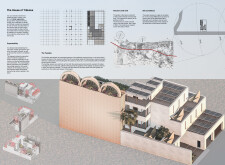
Located within an urban setting, the House of Tribulus integrates contemporary design principles with inspirations drawn from traditional Middle Eastern architecture. The project's intent is to create a functional and visually cohesive living environment that fosters community interaction. Unique elements of the design emphasize sustainability and cultural relevance, positioning the residence as an innovative response to local climatic and social contexts.
### Spatial Strategy
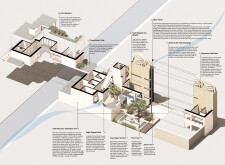
The design adopts the courtyard typology, traditionally prevalent in Middle Eastern homes, which serves as a central element for natural ventilation and promotes a connection between indoors and outdoors. The layout strategically utilizes the site’s orientation to maximize light and airflow, aligning with prevailing northwestern winds. Shading devices are incorporated to mitigate solar gain, optimizing comfort for residents while enhancing energy efficiency.
### Materiality and Sustainability
A carefully selected array of materials underpins the project's commitment to sustainability. Mud blocks are prominently used in the external walls for their thermal mass properties, contributing to cooler interiors. Concrete, plaster, and stucco complement the structure's integrity and aesthetic, while polystyrene serves as an effective thermal insulator. Notably, solar panels are integrated into the building’s design, supporting renewable energy generation. Additionally, roof gardens enhance biodiversity and assist in regulating temperature, further reinforcing the residence's sustainable framework. Each material choice reflects local availability and cultural practices, anchoring the design within its contextual landscape.
### Design Features
The House of Tribulus showcases an adaptable structural grid that accommodates future expansion as community needs evolve. The facades incorporate modern interpretations of traditional designs through perforated screens, providing both privacy and ventilation. Roof gardens serve as dual-purpose spaces for recreation and social engagement, reinforcing the project's focus on community living. The energy-efficient design elements, including photovoltaic cells and a passive cooling wind tower, contribute to a net-zero energy framework, exemplifying a holistic approach to sustainable architecture. Cultural motifs, such as the Mugarnas Half-Dome, ensure that the building resonates with local heritage while maintaining a modern identity.