5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
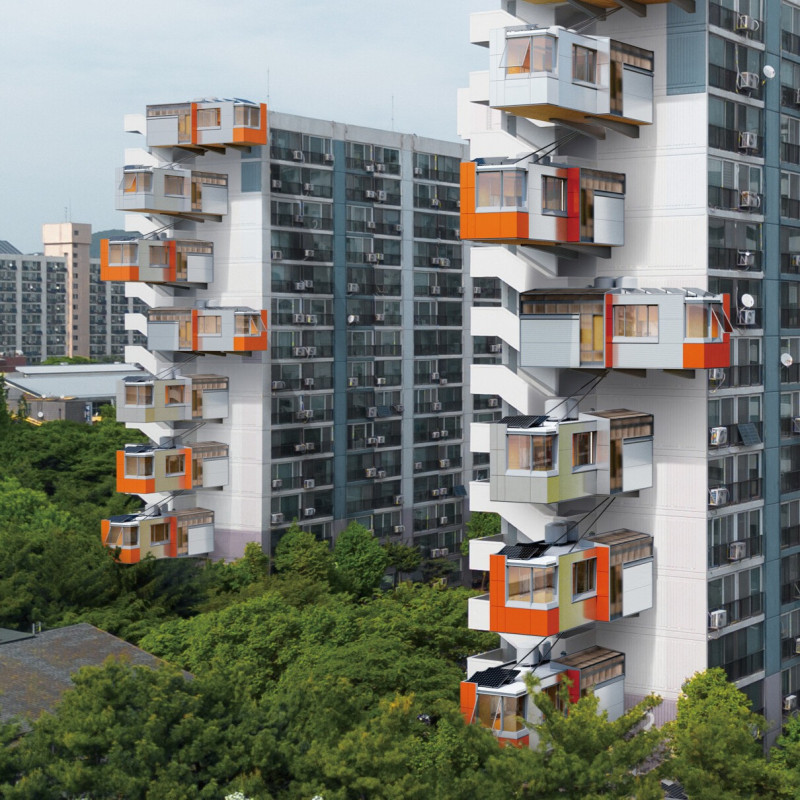
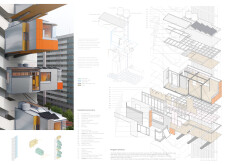
The "Parasitic Home" project responds to the housing crisis in South Korea, particularly within the densely populated district of Nowon-gu, Seoul. Accelerated urbanization following the Korean War has resulted in significant housing shortages, necessitating innovative architectural solutions. This initiative proposes an adaptive model for urban living by integrating modular housing units that extend pre-existing high-rise buildings. By enhancing individual living environments, this design promotes sustainability and fosters community interaction.
### Spatial Strategy and Modularity
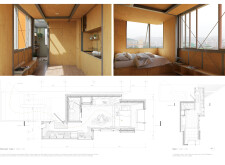
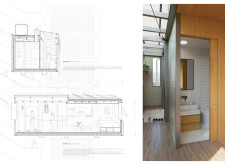
The central concept revolves around the notion of "parasitism," where modular housing units are affixed to existing structures, effectively utilizing vertical space in urban settings while minimizing land consumption. This approach addresses the urgent need for vertical living solutions in areas with high population density and creates flexible accommodation options. Residents can personalize their living spaces, facilitating a range of configurations that cater to diverse lifestyles and requirements.
### Materiality and Sustainable Features
Constructed using a selection of modern materials, the design prioritizes both functionality and sustainability. Key materials include:
- **Polystyrene Roofing:** Offers insulation and protection against weather elements.
- **Waterproofed Polyurethane Insulation Sheets:** Enhance thermal efficiency.
- **Metal Cladding Panels:** Provide durability and low maintenance.
- **Wood Finishes:** Introduce warmth to interior spaces.
- **Glass Windows:** Optimize natural light and encourage outdoor connectivity.
- **Solar Panels:** Facilitate renewable energy generation.
- **Rainwater Harvesting System:** Supports sustainable water management.
- **Precast Concrete Elements:** Form crucial structural components of the existing buildings.
These components collectively support the project's commitment to reducing environmental impact while improving the quality of life for residents. The design emphasizes ample natural light through large windows and skylights, enhancing overall well-being within the living spaces.