5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
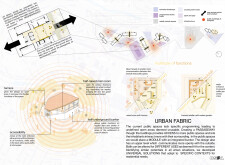
The architectural design project focuses on improving existing residential structures in Saltivka, a neighborhood characterized by challenges related to spatial efficiency and livability. The primary intent is to implement a "RETROFIT-SYSTEM" that enhances the functionality and aesthetic appeal of these blocks while promoting community interaction. This approach integrates current structures with new modular designs to address diverse resident needs without extensive demolition or disruption.
## Spatial Strategy and Community Engagement
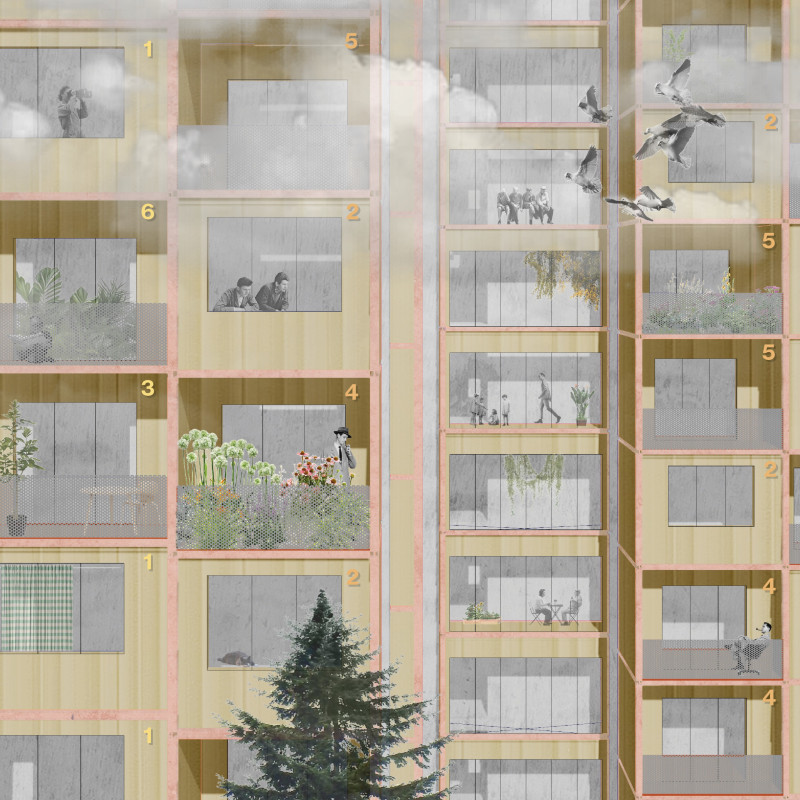
The project’s spatial strategy emphasizes the activation of underutilized areas, particularly dysfunctional winter gardens and communal spaces. By refining these typologies, the design aims to optimize light quality and usability, transforming winter gardens into vibrant spaces for leisure while enhancing communal areas into hubs for social interaction. A comprehensive analysis of individual blocks informs the development of a "universal toolkit," comprising modular elements with adjustable depths and adaptable façades, which allows for tailored responses to user requirements while maintaining a cohesive architectural language.
## Materiality and Design Flexibility
The choice of materials is grounded in modern building practices that underscore sustainability and functionality. The structural framework incorporates steel frames for integrity, lightweight concrete for walls and ceilings, and glass panels to facilitate natural light and visual connections to the outdoors. Wood elements are utilized in shared spaces to introduce warmth and acoustic benefits. The flexibility inherent in the modular design not only accommodates specific user preferences but also integrates public and private domains, enhancing movement and connectivity throughout Saltivka. Public modules are designed to serve multiple functions, including cafes and libraries, fostering diverse communal activities.