5 key facts about this project
# Architectural Analysis Report: House of the Future
## Overview
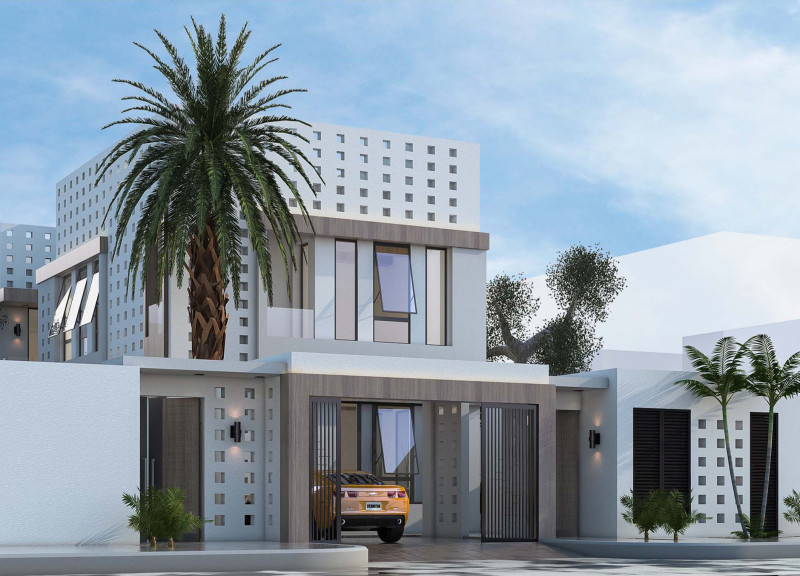
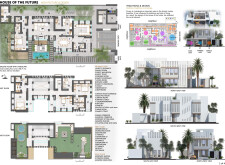
Located in Al Barsha, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the House of the Future is a residential design that reflects the region's dual identity of modern innovation and cultural heritage. This project leverages its strategic urban setting, providing access to essential amenities such as healthcare, markets, and educational institutions, while ensuring the design respects and incorporates elements of traditional Emirati architecture.
## Architectural Form and Materiality
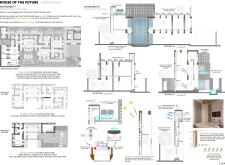
The architectural form features contemporary lines and design elements that resonate with local traditions through an intricate façade of exposed walls and alternating voids. This approach incorporates domed ceiling structures to enhance natural light distribution within the interior spaces. Material choices emphasize sustainability and aesthetic appeal; recycled bricks, sourced from drilling by-products, provide durability with reduced environmental impact, while expansive glass openings facilitate natural light and connect occupants with the landscape. The use of natural stone and wood harmonizes the interiors with the desert environment, complemented by LED lighting for energy efficiency.
## Sustainability and User Experience
Sustainability is a core aspect of the design, evidenced by the strategic installation of solar panels and rainwater harvesting systems. Drip irrigation systems optimize water use, while a green roof aids in natural cooling and mitigates urban heat. The layout supports flexibility for future expansions, aligning with the values of family progression in Emirati culture. Interior spaces prioritize well-being through a minimalist approach enriched with natural textures and colors, creating a balanced relationship between indoor and outdoor areas for enhanced user experience. Additionally, the landscape integrates native flora, such as the Tamarl palm, and establishes outdoor seating spaces from natural stone, fostering social interaction while complementing the local environment.