5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
Situated within a desert context, the House of the Future represents a synthesis of contemporary architectural design and sustainable living practices. The intent of this project is to create a residential environment that harmonizes with its natural surroundings while addressing the unique climatic challenges of the region. The design incorporates modern materials and innovative aesthetics to promote energy efficiency and environmental stewardship.
### Zoning and Functional Layout
The spatial organization of the residence utilizes a clear zoning strategy that divides the interior into distinct private and social areas. Private spaces, located on the upper floors, consist of bedrooms and personal areas that offer tranquility and seclusion. Conversely, ground-level social areas are designed for communal gatherings and interactions, fostering family connections. Additionally, the incorporation of multiple gardens not only enhances the living experience through natural landscapes but also contributes to the overall well-being of the occupants.
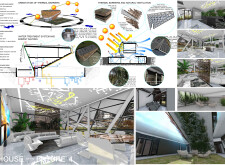
### Materiality and Sustainability Features
The selection of materials for the House of the Future underscores its commitment to sustainability and environmental integration. Oxidized micro-perforated sheet metal serves as an innovative exterior, providing solar protection and facilitating natural ventilation. Photovoltaic panels on the double roof contribute to energy efficiency, while locally sourced stone minimizes the ecological footprint of the construction. Advanced thermal barriers, comprising materials such as aluminum and polystyrene, effectively regulate indoor temperatures. The design also emphasizes sustainability through geothermal construction techniques, graywater recycling, and natural ventilation systems, reducing reliance on mechanical heating and cooling.
This architectural project stands out for its cultural resonance, marrying traditional motifs with modern design to create a sensitive and contextually aware living space. By embracing nature through the integration of gardens and vertical climbing plants, the structure blurs the boundaries between indoor and outdoor environments, promoting biodiversity and enhancing the overall quality of life for its occupants.