5 key facts about this project
## Overview
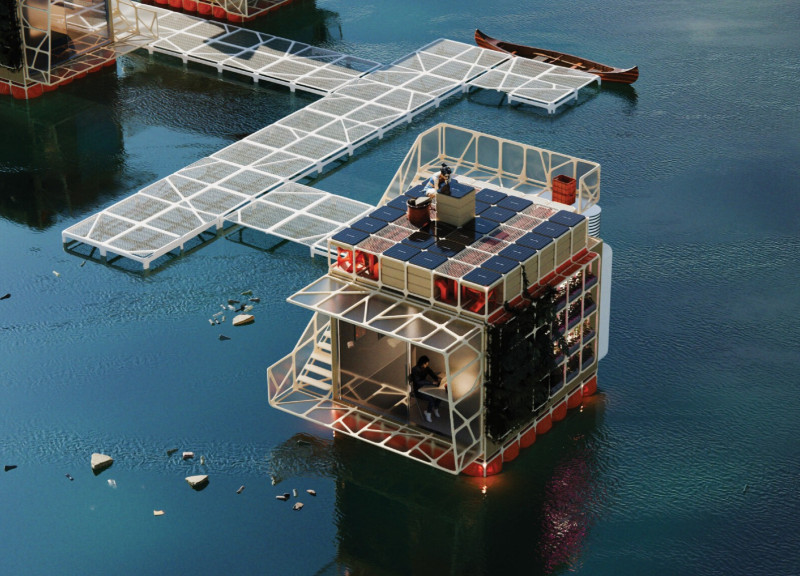
PLAST-X addresses the critical issue of plastic pollution in marine environments through an innovative architectural approach. The design is located in a future housing framework aimed at sustainable and adaptable living spaces. By utilizing recycled materials, the project emphasizes resource regeneration while responding to contemporary societal needs, reinforcing the significance of ecological awareness in architectural practice.
### Spatial Strategy and Resilience
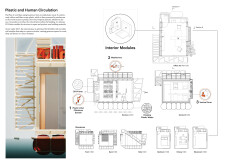
The PLAST-X project features a compact, 25-square-meter living module designed to float on water, addressing the challenges posed by rising sea levels and potential flooding due to climate change. This buoyant structure exemplifies adaptability to fluctuating water levels, ensuring resilience in a dynamic environment. Moreover, the design incorporates vertical farming systems that support food production and security, utilizing mealworms that convert plastic waste into compost, thereby creating a closed-loop ecosystem.
### Materiality and Technological Integration
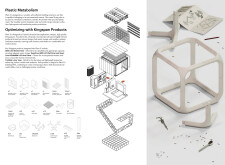
A key element of the PLAST-X design is the thoughtful selection of materials aimed at minimizing environmental impact. The main structural components include recycled plastic, wood products for interior resilience, and aerated concrete panels to enhance thermal efficiency. Solar panels provide renewable energy, while 3D printing technology allows for the fabrication of parts from recycled plastics, facilitating both creativity and rapid construction. This material combination not only ensures the structural integrity of the design but also reinforces a commitment to sustainability by promoting a circular economy within housing.