5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
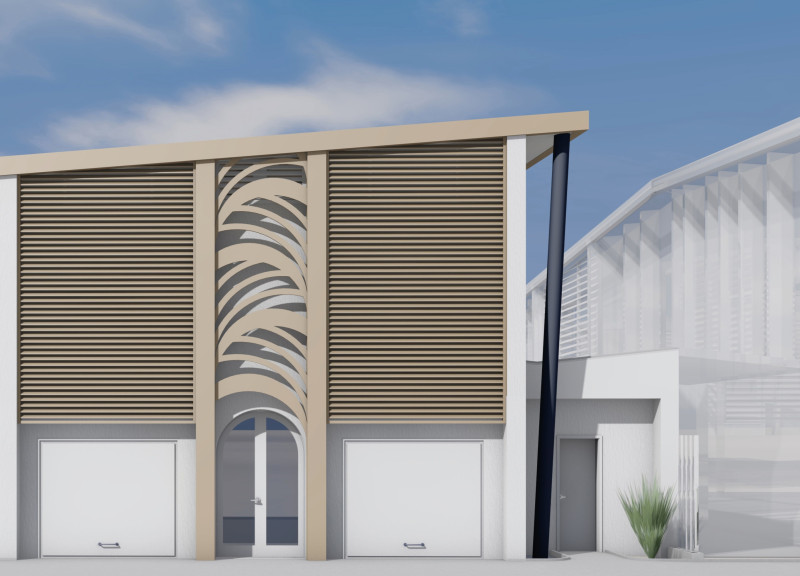
The House of the Future is located in a desert region where its design prioritizes sustainability and functionality within a harsh climate. Drawing inspiration from traditional desert dwellings while incorporating contemporary architectural techniques, the project aims to create a harmonious blend of aesthetics and practicality. The architectural intent focuses on energy efficiency and cultural relevance, utilizing innovative materials to address environmental challenges distinctive to the area.
## Structural Configuration and Materiality
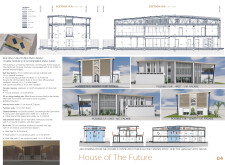
The building employs a masonry reinforced concrete pillar frame, providing a robust structural foundation that allows for future flexibility in the ground plan. The roof is designed to accommodate solar panels, underscoring the commitment to renewable energy sources. Natural ventilation strategies have been integrated to promote air circulation, facilitating cooler environments within living spaces.
A variety of materials have been carefully chosen for their durability and sustainability, including reinforced concrete blocks for the structural frame, insulated standing seam sandwich panels for roofing, and autoclaved aerated concrete blocks for the facade. Double-glazed units enhance energy performance, while mineral wool insulation contributes to both thermal and acoustic efficiency.
## Spatial Arrangement and User Experience
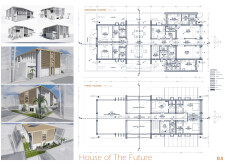
The organization of internal spaces reflects a systematic approach that balances privacy and communal interaction. The ground floor features designated living areas, bedrooms, and garden spaces, promoting both family engagement and personal retreat. On the first floor, additional bedrooms and workspaces encourage collaboration among residents, maintaining a functional layout that adapts to daily activities.
Noteworthy features include louvred blinds, which facilitate the collection of morning mist for irrigation, and an attic space designed for passive cooling, enhancing indoor comfort without excessive reliance on mechanical systems. The design's inherent flexibility allows for future modifications to adapt to the evolving needs of its occupants, ensuring long-term usability and relevance.