5 key facts about this project
## Overview
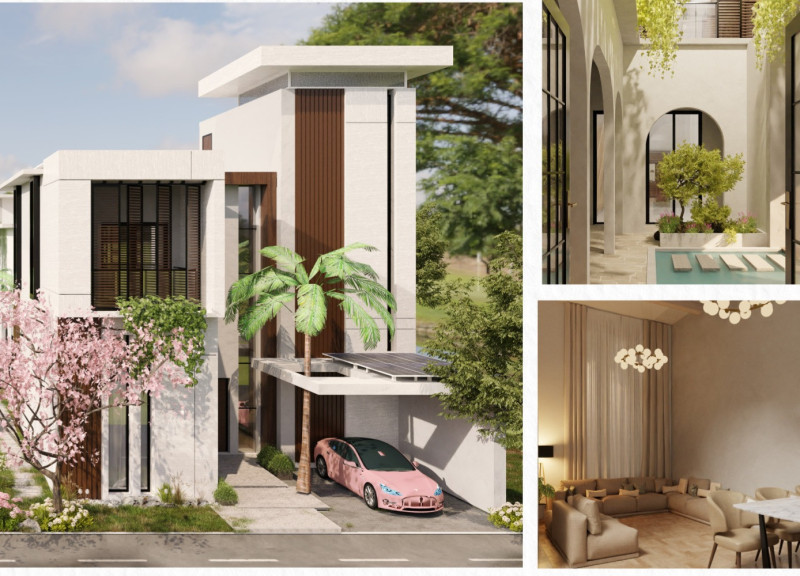
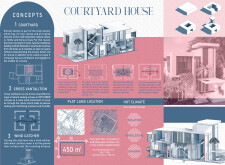
Located in the Al Zahia neighborhood of Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, the Courtyard House merges traditional Emirati architecture with contemporary sustainable practices. The design prioritizes family cohesion and privacy, central to Emirati cultural values, while also addressing environmental considerations. The incorporation of a courtyard not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also serves practical functions that improve indoor living conditions.
## Spatial Strategy
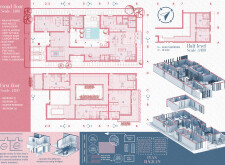
The spatial organization is characterized by a distinctly functional layout. On the ground floor, shared living areas and service spaces are arranged to facilitate interaction while preserving privacy through designated zones. The courtyard, positioned at the heart of the design, provides natural light and ventilation, functioning as a communal gathering area. The first floor focuses on private quarters, including bedrooms designed for comfort and tranquility, with strategic window placements to maximize natural lighting. An optional second floor allows for future expansion, integrating a rooftop terrace to enhance outdoor living opportunities.
## Material Selection and Sustainability
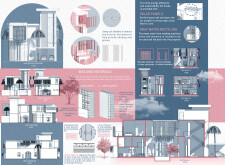
The choice of materials reflects both functionality and ecological responsibility. Limestone is utilized for walls, offering durability and natural thermal insulation. Lime plaster is employed for interior finishes, promoting humidity control essential for the climate. The building features solar panels, contributing to energy efficiency, while clay bricks used for exterior finishes enhance thermal performance. Interior materials, such as wood and fiberglass insulation, add warmth and comfort, while design elements like air gaps and water barriers bolster moisture management. Collectively, these choices support not only the sustainability objectives of the project but also its alignment with traditional design principles in a modern context.