5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
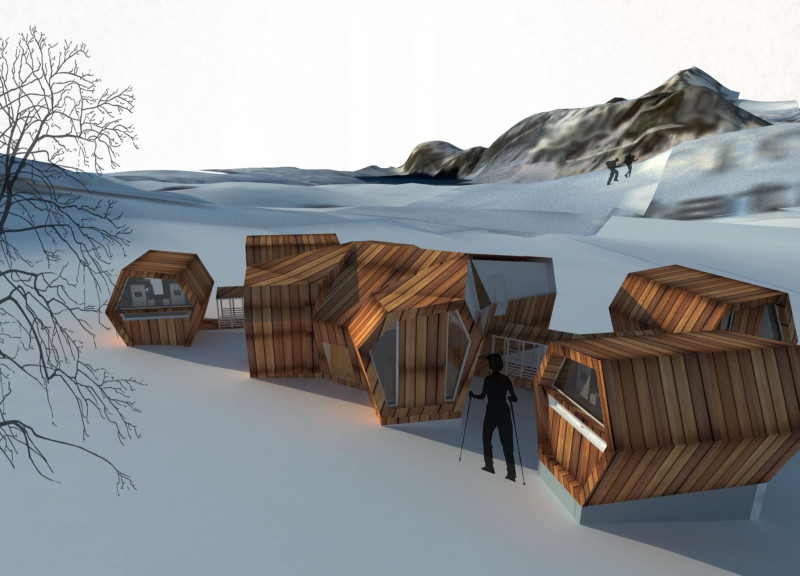
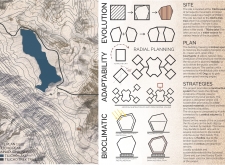
Situated in the Annapurna region of Nepal, near the renowned Tilicho Peak, the design addresses the unique challenges of high-altitude living. The intent is to create a structure that harmonizes with its mountainous environment while employing sustainable materials and architectural strategies. The project emphasizes resilience and functionality, ensuring it meets the demanding climatic conditions of an elevation of approximately 7,000 meters.
### Spatial Organization and User Engagement
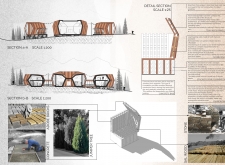
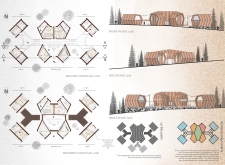
The architectural layout employs radial planning to facilitate interconnected, modular units centered around a communal core. This design not only decreases the building's ecological footprint but also fosters social interaction through semi-open spaces that encourage communal living. Hexagonal units are arranged to optimize natural light and ventilation, providing a spatial experience that aligns with user needs while respecting the site's topography.
### Material Selection and Environmental Integration
The structure incorporates a variety of materials selected for their performance and local availability. A concrete base offers stability and thermal efficiency, while adobe bricks provide significant thermal mass conducive to temperature regulation. Teak and sal wood are utilized for their aesthetic and durable properties, contributing to both insulation and structural integrity. Additionally, juniper branches serve as an insulating layer in the walls, enhancing thermal comfort, and stone foundations support structural stability while integrating seamlessly with the local geology. This material strategy prioritizes sustainability by minimizing transportation impacts and supporting local employment in the construction process.