5 key facts about this project
## Architectural Design Project Analysis Report
### Project Overview
Located within the Himalayan region, this design initiative responds to the distinct climatic and topographical challenges posed by steep terrains. Emphasizing cultural resonance, the building engages with the architectural traditions of local Tibetan communities while accommodating contemporary needs for residents and visitors.
### Site Strategy
#### Geographical Context
The selected site, situated at varying altitudes, showcases unique climatic characteristics that inform the architectural approach. At elevations above 3000 meters, Tibetan culture predominates, while the mid-range of 3000 to 750 meters reflects a mix of Tibetan and Indian influences. Below 750 meters, other ethnic groups reside, necessitating a design that respects these physical and cultural divisions. The architectural strategy aims to integrate seamlessly with the natural landscape, considering topographical variations.
#### Topographical Adaptation
Design solutions demonstrate a strong relationship with the mountainous terrain. Key features include:
- Orientation that maximizes solar exposure, essential for heat retention in harsh climates.
- A stepped foundation that facilitates natural snow clearance and structural stability against avalanches.
### Design Development
#### Conceptual Framework
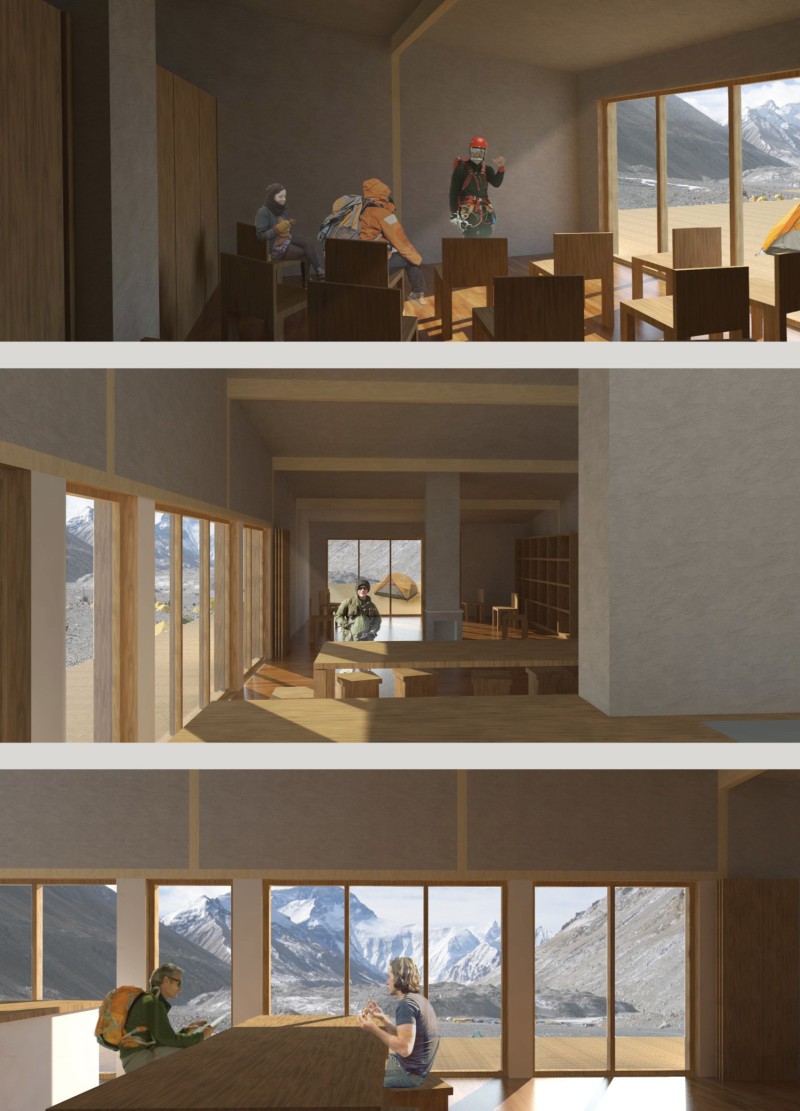
The building is designed to function as a multi-use space, combining communal areas, sleeping quarters, and a refuge for trekkers. This arrangement fosters social interaction while providing essential services.
#### Key Design Elements
1. **Façade Orientation**: A longer south-facing façade is aimed at optimizing sunlight capture.
2. **Daylight and Views**: Large openings enhance natural light and frame views of the surrounding landscape.
3. **Outdoor Spaces**: Decks are included to promote visitor engagement with nature during favorable weather.
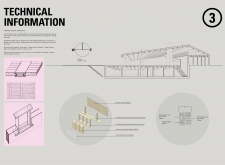
### Materiality
#### Material Choices
Materials are selected based on local availability and sustainability:
- **Locally Sourced Timber**: Utilized for structural framing, reducing environmental impact.
- **Straw Bale Insulation**: Chosen for its thermal efficiency.
- **Lime Render**: Provides durability and weather resistance suited to the region’s conditions.
- **Stone Walls**: Incorporated to enhance thermal mass and align with traditional aesthetics.
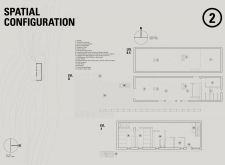
### Spatial Configuration
#### Floor Plans
The project encompasses multiple levels with distinct functions:
- **Ground Level**: Contains communal facilities and kitchens, facilitating user interaction.
- **Upper Levels**: Feature sleeping areas and communal spaces with expansive views to enhance the user experience.
#### Functional Zoning
Efficient zoning allows for a clear division of functions:
- **Communal Spaces**: Located on lower levels to promote community interaction, while private areas are positioned above for privacy.
- **Adaptability**: Spaces are designed for multi-purpose use, enabling a range of activities from gatherings to educational sessions.
### Design Outcomes
#### Integration with the Environment
The design is closely aligned with its geographical context, reflecting local culture and climate through informed architectural choices.
#### User Experience
Emphasizing comfort and accessibility, the design adapts to the varying needs of trekkers and locals. Natural lighting, communal spaces, and unobstructed views contribute to an enhanced user experience, promoting a sense of community.
### Unique Aspects
- **Cultural Relevance**: The project incorporates traditional Tibetan architectural elements while employing modern construction techniques.
- **Sustainable Approach**: The use of local materials minimizes the carbon footprint and aligns with sustainability objectives.
- **Adaptability**: Flexible spaces accommodate diverse functions, catering to seasonal variations and user demands.