5 key facts about this project
## Project Overview
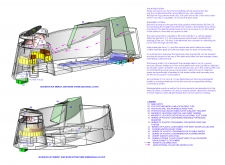
The Mountain Hut is situated in a mountainous region and is designed to function as a self-sufficient living space that emphasizes sustainable energy and water systems. The project prioritizes ecological responsibility by aligning its design with local climate dynamics and resource availability. It serves as a model for responsible architecture, integrating functionality with an awareness of environmental impact.
## Water Management System
The water management system is designed to efficiently harness local resources. It features fog catchment systems that collect moisture through specially installed mesh, enabling the retrieval of water from the environment. Grey water recycling mechanisms have been included to minimize waste and promote sustainability. Infrastructure components have been meticulously designed to ensure optimal operation, incorporating containers for both potable and non-potable water.
## Energy Generation Strategy
The energy generation strategy is anchored in renewable sources. Photovoltaic solar panels are strategically positioned to track sunlight and maximize solar energy collection, while a vertical axis wind turbine adds another layer of renewable energy capture. This dual approach reflects a robust commitment to energy efficiency.
## Material Selection and Spatial Organization
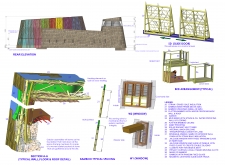
Material selection plays a crucial role in the hut's design integrity, with an emphasis on sustainability. Bamboo serves as a primary structural element due to its lightweight and resilient properties, while gabion walls, constructed from local stones, provide stability and connect the structure to its geological context. Additionally, the interior layout features interconnected spaces that promote accessibility and facilitate social interaction among occupants, incorporating natural light and ventilation for enhanced user experience.
Focal points in the design include stained glass panels and a wooden façade, which create exterior texture and color. Special attention to the cohesive relationship between interior and exterior elements reinforces the hut's integration with its surroundings, reflecting principles of ecological sustainability.
Key innovations include a solar panel tracking system for enhanced energy capture and provisions for biogas digestion systems to manage organic waste effectively. The multifunctional design additionally supports community resilience by fostering social interaction within a framework of renewable energy and sustainable living practices.
### Materials Used
- Bamboo
- Gabion baskets (filled with local stones)
- Photovoltaic solar panels
- Vertical axis wind turbine
- Recycled plastic bottles
- Light steel for framework
- Fiberglass for structural components
- Straw and grass bales for insulation
- Heating elements for snow melting on roofs