5 key facts about this project
## Overview
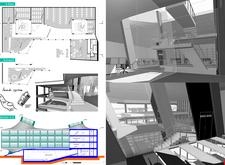
Tokyo POP Lab serves as a multi-purpose educational hub located in Tokyo, Japan, distinctly designed to foster creativity, collaboration, and community engagement. This facility features a multi-story structure with a range of spaces tailored for learning, social interaction, and technological innovation. Its architectural design reflects both contemporary aesthetics and function-driven principles, situating itself within the vibrant urban fabric of Tokyo.
## Architectural Form and Materiality
The building’s exterior is characterized by an undulating facade that conveys a sense of movement, symbolizing the ongoing evolution of ideas and collaboration. Large signage displaying "POP Lab" is integrated into the facade, providing visibility while complementing the overall design. Extensive glazing is employed to maximize natural light, creating dynamic interior environments through a deliberate play of light and shadow. Complementing the glass are reflective aluminum panels which respond to the surrounding urban context, reinforcing the modern character of the building. The use of reinforced concrete contributes to the structural integrity, serving as a stable foundation for diverse functional areas.
## Spatial Strategy and User Engagement
The spatial organization prioritizes user experience through deliberate zoning of activities over several floors. The ground floor features an open lobby that serves as a versatile space for exhibitions and events, encouraging spontaneous interactions among visitors. Classrooms, design studios, and conference rooms are purposefully integrated to adapt to various educational methodologies, showcasing flexibility in design. Additionally, dedicated resource areas, such as libraries, foster self-directed learning. Indoor and outdoor green spaces, including landscaped terraces, enhance the overall user experience, promoting a connection with nature throughout the facility.
Sustainability is a core component of the design, featuring green roofs and rainwater harvesting systems that reduce the ecological footprint and enhance occupant well-being. The building is equipped with energy-efficient materials, further contributing to its sustainable objectives.