5 key facts about this project
## Overview of the Project
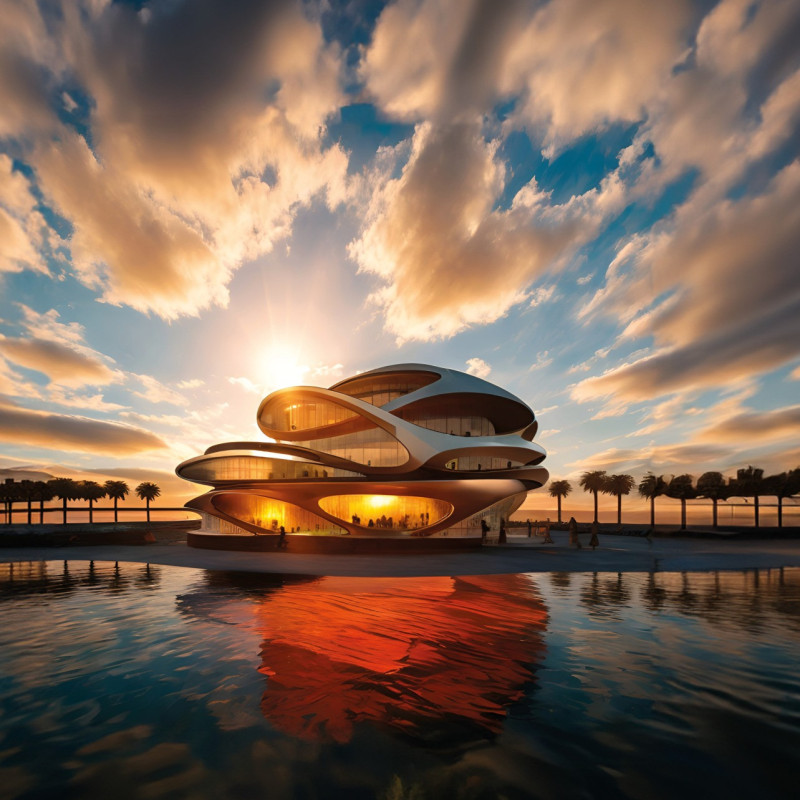
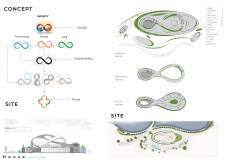
Located in a contemporary urban setting, the Infinity House exemplifies modern residential design through its innovative approach to sustainability and technology integration. The project not only addresses the needs of modern families but also reflects a commitment to ecological mindfulness. The central theme revolves around creating a harmonious relationship between the living spaces and the natural environment, embodying principles of continuity and connection.
## Design Concept: Flow and Interconnection
The architectural design is characterized by a flowing, organic form that evokes the motif of infinity, symbolizing uninterrupted connectivity among family members and the environment. The spatial organization features a series of interconnected areas, promoting fluid movement throughout the residence. Key living spaces, including the kitchen and living room, are strategically positioned to maximize natural light and offer views of the surrounding landscape, enhancing the indoor-outdoor experience.
## Material and Environmental Integration
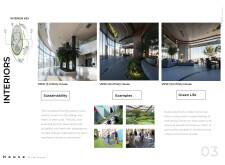
The use of sustainable materials is paramount in the project. Steel and extensive glass facades provide structural integrity and transparency, permitting abundant natural light while fostering a visual connection with nature. The incorporation of living green walls enhances the building's aesthetic appeal and contributes to improved air quality and temperature regulation. Biophilic design elements, including indoor vegetation, further promote mental well-being, creating a serene living environment.
Innovative technologies, such as piezoelectric flooring, are implemented to generate renewable energy through everyday movement, reinforcing the project's commitment to environmental sustainability. The overall design and material choices not only establish a sophisticated aesthetic but also prioritize energy efficiency and minimal ecological impact throughout the lifecycle of the building.