5 key facts about this project
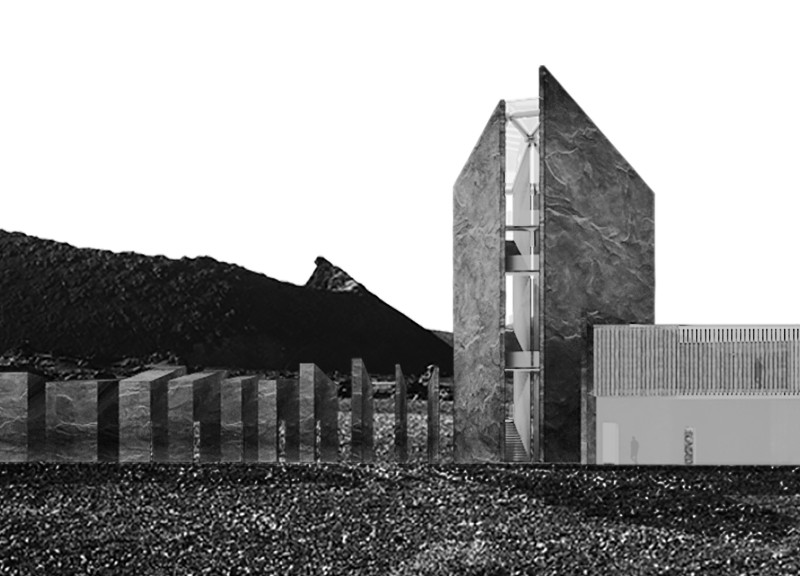
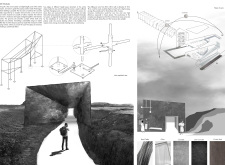
The project is located in the unique landscape of Grjótagjà, which is marked by its significant geological features. The goal is to enhance visitor engagement with this natural environment through a design that harmonizes with the setting. The layout includes various functional spaces, such as access areas, a parking facility, service buildings, and a central observation tower. The overall design concept aligns closely with the tectonic characteristics of the landscape, allowing the architecture to work alongside nature rather than compete with it.
Observation Tower
A key element in the design is the observation tower named Rifa, a term that translates to "fissure" in Icelandic. This tower serves as a focal point for visitors, inviting them to experience the landscape from an elevated perspective. The entryway reflects the natural fissures found in the area, creating an immediate connection to the geological history. The tower allows visitors to observe the surrounding beauty, linking the architectural experience to the landscape itself.
Accessibility Framework
Accessibility is an important consideration in the design. The project features facilities such as changing rooms and relaxation areas strategically placed to serve a broad range of visitors. This thoughtful arrangement ensures that everyone can easily access various parts of the site. By focusing on inclusivity, the design encourages individuals and families to explore and enjoy the natural surroundings comfortably.
Pathways and Connectivity
The pathways within the design are both modular and lightweight. They guide visitors to important areas, including the bathing location at Kvennagjà cave. These paths are designed to blend into the landscape while remaining functional. By maintaining clear routes, visitors can easily navigate the space and appreciate the surrounding natural beauty. The design promotes engagement with the site, allowing exploration without unnecessary barriers.
Material Considerations
The materials chosen for the project include reinforced concrete and corten steel. These materials contribute to the structural integrity of the observation tower while maintaining a connection to the geological context. Glass elements are also used to enhance the experience, allowing for expansive views of the outdoors. In addition, energy-efficient solutions, such as heat pumps and vertical geothermal probes, reflect a commitment to environmental considerations in the design.
The observation tower’s entry, characterized by its fissured form, welcomes visitors into a space that echoes the landscape's natural dynamics. It invites exploration and connection, bridging the gap between architecture and the surrounding environment.