5 key facts about this project
### Project Overview
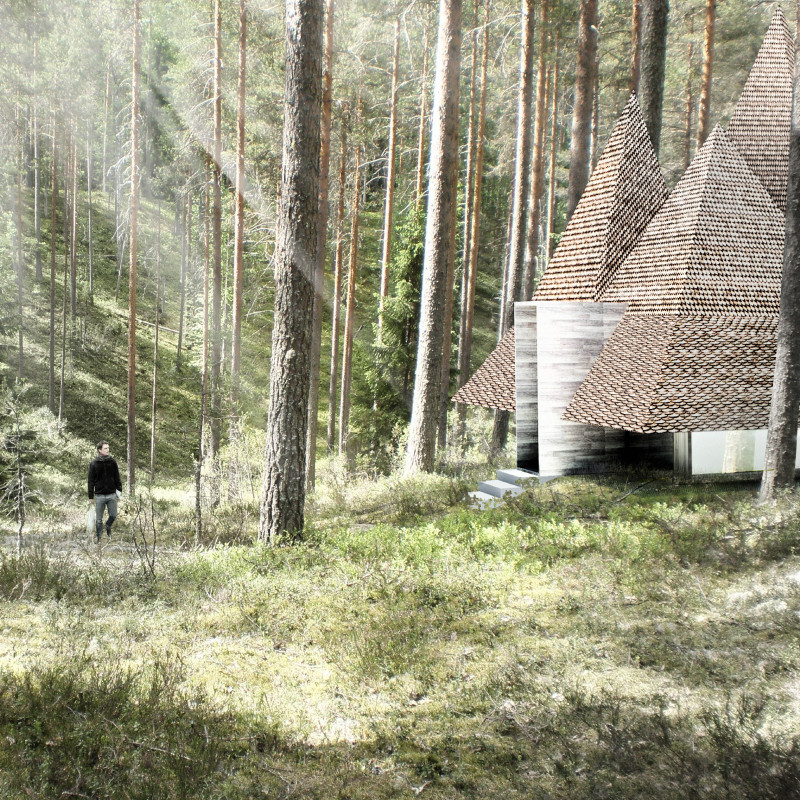
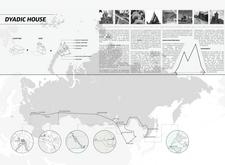
The Dyadic House is situated along the Trans-Siberian Railroad, integrating cultural narratives with contemporary architectural practices. This design draws inspiration from traditional Russian vernacular architecture, creating a residence that is attuned to its geographical context while addressing modern requirements for sustainability and functionality.
### Spatial Strategy
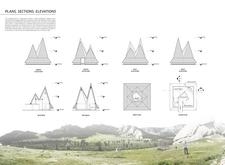
The layout of the Dyadic House revolves around a polygonal courtyard, fostering communal interaction and allowing natural movement throughout the space. The structure features peaked roofs that not only serve practical purposes such as snow shedding but also contribute to its overall aesthetic. Internally, the design maximizes natural light through tall, angled windows that frame views of the surrounding landscape, enhancing the connection between indoor and outdoor environments.
### Materiality and Sustainability
The construction of the Dyadic House utilizes materials selected for both their sustainability and regional relevance. Timber sourced from sustainable forests serves as the primary material, reinforcing the architectural identity and aligning with local traditions. A solid stone foundation provides stability and thermal performance while handcrafted wooden shingles cover the roofs, ensuring durability and reflecting traditional craftsmanship. Additionally, the design employs advanced structural techniques and local production methods, including CNC milling for precision and artisanal techniques for customization, supporting community engagement and sustainable practices throughout the construction process.