5 key facts about this project
### Overview
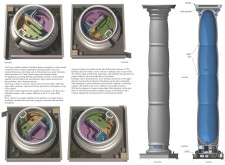
Located in diverse urban contexts, the design focuses on residential units called "Gondolas" and "Aerostats," emphasizing sustainability and autonomy. The intent is to create adaptable and transportable living environments that minimize reliance on traditional infrastructural systems. By elevating living spaces, the project seeks to blend functional living with ecological sensitivity.
### Spatial Organization and Flexibility
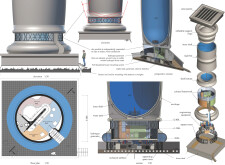
The design elevates living units by 2.5 to 3.0 tons above ground, eliminating the need for conventional foundations. This innovative elevation facilitates strategic placement within varying urban landscapes and natural reserves, allowing for flexible integration with the environment. The interior is organized in circular arrangements, enhancing spatial efficiency and promoting natural ventilation and daylight access.
### Materiality and Sustainability
The construction employs advanced materials, including a 3D-printed framework for lightweight structural integrity and a double kerf shell for the Aerostat units, using a safe hydrogen and helium mixture. Future proposals introduce high-strength carbon fiber to further reduce the environmental impact. The systems incorporate solar panels for energy self-sufficiency, alongside integrated septic tanks and water generators for effective waste management and resource recycling. This cohesive approach to material use not only prioritizes sustainability but also supports eco-friendly living practices.