5 key facts about this project
## Overview
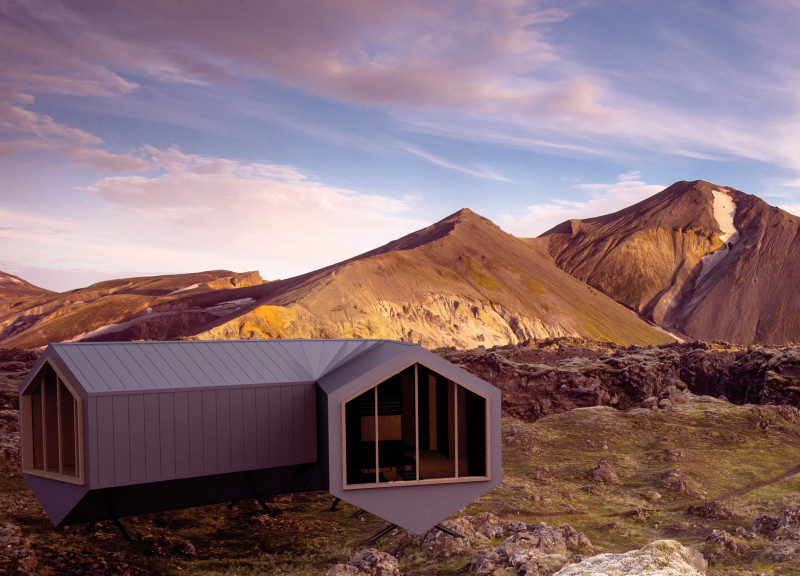
The Iceland Excursion Module (IEM) is an architectural design focused on delivering efficient living solutions within extreme climates, specifically in Iceland. The intent is to create a compact structure that harmonizes with the unique characteristics of the surrounding landscape while promoting sustainability and self-sufficiency. The design integrates modular systems and innovative strategies to address the challenges posed by the harsh environment.
### Spatial Configuration
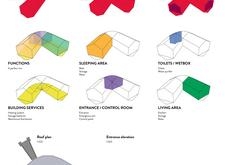
The spatial organization of the IEM is thoughtfully arranged to accommodate various functions, enhancing usability while maintaining comfort. Key areas include:
- **Sleeping Area**: Designed to house up to 12 individuals, this space incorporates practical storage solutions to optimize functionality.
- **Restroom Facilities**: Featuring compact toilets and a water purification system, this area is essential for sustainable living.
- **Entrance/Control Room**: Serving as both entry and the operational hub, this room manages essential systems, ensuring user security and convenience.
- **Living Area**: A multifunctional space that includes a kitchen and dining zone, fostering social interaction and daily activities.
### Material Selection
The materials chosen for the IEM play a critical role in its structural performance and environmental compatibility:
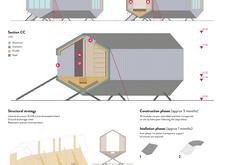
- **Cross-Laminated Timber (XLAM)**: Acting as the primary structural element, XLAM provides a strong yet lightweight framework that is also environmentally sustainable.
- **Steel**: Used for structural anchorage, enhancing stability.
- **Aluminum**: Applied to the external facade for its durability and lightweight characteristics.
- **Insulation**: Essential for maintaining a comfortable internal climate amidst external extremes.
- **Precast Concrete Beams**: These elements form a stable foundation, contributing to the overall integrity of the module.
The design strategy includes unique features such as an elevated base to adapt to uneven terrain and an energy-efficient setup involving solar panels and turbines, promoting self-sufficiency. Large windows optimize views of the Icelandic landscape, while wood finishes in the interior create an inviting atmosphere conducive to community and relaxation.