5 key facts about this project
# Heritage Housing Along the Prypiat River: Project Report
## Project Overview
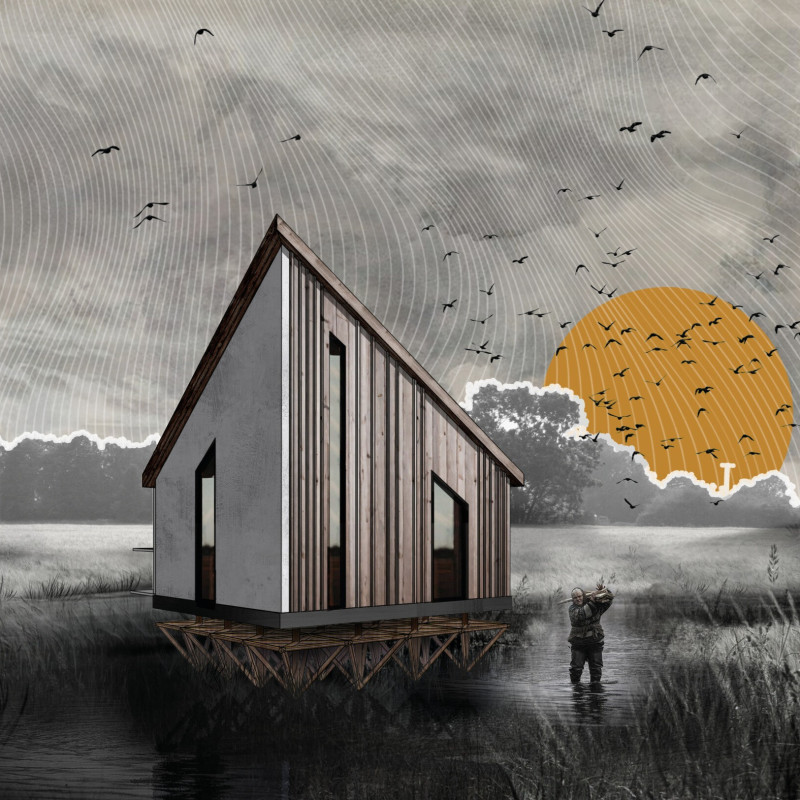
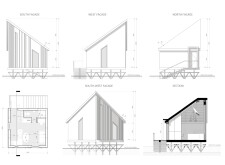
Located in the Palesie region along the Prypiat River, the design addresses housing needs influenced by cyclical spring flooding. Drawing inspiration from traditional local architecture, particularly the _hut_, the concept emphasizes a new MICRO home that balances functional requirements with cultural relevance. The project seeks to integrate local heritage with contemporary engineering practices to create resilient living spaces.
## Resilience and Cultural Integration
The primary aim is to construct a sustainable and secure dwelling that meets the challenges of seasonal flooding. This project respects and evokes local traditions while employing modern methodologies to enhance livability. A significant design feature is the incorporation of a _pawluk_, a diamond-shaped structure that is integrated into the foundation. This element not only offers protection and safety but also signifies cultural identity by connecting the architecture to spiritual narratives historically associated with these constructs.
## Material Selection and Structural Features
The choice of materials reflects a blend of traditional and modern elements focused on safety, durability, and ecological responsibility. Concrete provides strength and flood resistance to the foundation, while wooden façades pay homage to local aesthetics and cultural practices. Steel reinforces structural stability, essential for elevated living conditions, and glass elements allow ample natural light, fostering a connection with the environment.
Key design attributes include an elevated structure, lifted above expected flood levels, enhancing accessibility and engagement with the surrounding landscape. The pitched roof design efficiently manages snow and rainwater, merging functionality with visual appeal. Additionally, the modular framework allows for relocation during flooding events, aligning the dwelling with local adaptive practices historically employed in the region.
The design process employed extensive analysis of historical flooding patterns and cultural housing techniques, which informed critical decisions regarding structural elevation and overall resilience strategies. Artificial intelligence was utilized to enhance facade designs and optimize energy systems, marrying traditional insights with cutting-edge technologies to reduce environmental impacts and minimize costs.
Overall, the project embodies a careful consideration of community needs, cultural heritage, and environmental challenges, demonstrating a forward-thinking approach to architectural design in vulnerable regions.