5 key facts about this project
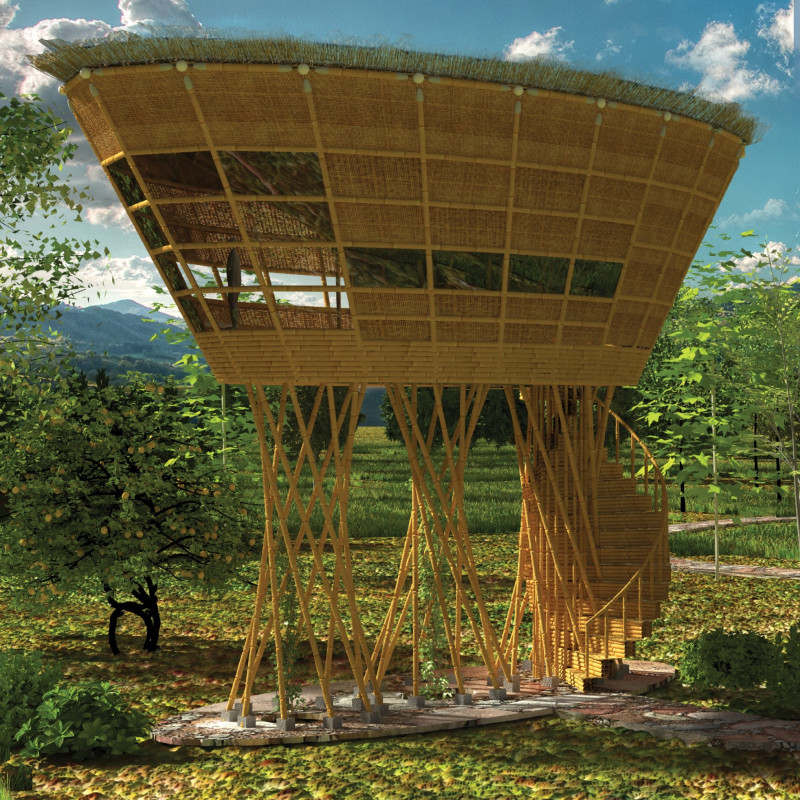
The Uplift project, located in Kep Province, Cambodia, is a notable architectural endeavor that addresses the need for sustainable rural tourism while respecting the local environment. This initiative focuses on creating a series of elevated bamboo huts intended for relaxation and communal activities. By implementing eco-friendly materials and innovative design principles, the Uplift project successfully integrates human habitation with the natural landscape, enhancing both user experience and environmental preservation.
The project aims to cultivate a space that fosters community engagement and promotes ecological awareness. Each hut is situated to maximize views of the surrounding hills and greenery, fostering a strong connection with nature. The elevated design minimizes the impact on the ground, promoting an environment that can adapt to seasonal shifts in climate while sustaining local biodiversity.
Material Usage and Structure
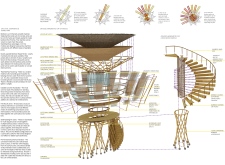
The Uplift project primarily utilizes bamboo as its core construction material. Known for its rapid growth and renewability, bamboo enhances the project's sustainability profile. It is combined with thatch roofing, providing insulation and visual appeal that aligns with local traditions. Concrete foundations support the huts, ensuring a stable base while allowing flexibility in the use of lighter materials above.
The architectural structure employs a hyperboloid form, efficiently distributing loads while maximizing space. This geometric approach not only enhances structural integrity but also allows for generous natural light penetration. The innovative use of pre-tensioned connections and rotating joint systems demonstrates a modern understanding of material properties, which complements the traditional aspects of bamboo construction.
Community-Centric Design
The Uplift project emphasizes its role as a community hub by incorporating multipurpose halls within the huts. These flexible spaces cater to both individual reflection and collective gatherings, reinforcing social interaction among visitors. Private sleeping quarters are designed to provide comfort while maintaining visual openness to the landscape, thereby enhancing the overall experience of tranquility.
The architectural design choices prioritize airflow and natural light, employing glazed panels and fabric dividers that adapt to both privacy and communal needs. This versatility is critical in establishing an environment conducive to mindfulness activities, such as meditation and yoga.
The emphasis on local craftsmanship not only supports economic growth but also preserves traditional building techniques. By integrating these elements, the Uplift project stands as an exemplary model of how architecture can function as a catalyst for sustainable practices within rural communities.
For further details on the architectural plans, architectural sections, and architectural designs of the Uplift project, interested readers can explore the project presentation for deeper insights into its functional and aesthetic components. This examination of the project provides an opportunity to understand the architectural ideas that inform its design and execution.