5 key facts about this project
## Overview
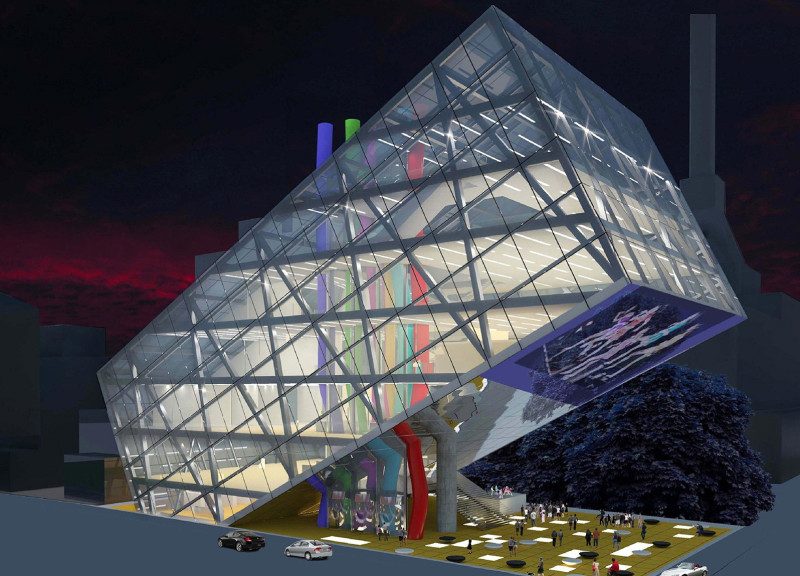
Located in Tokyo, Japan, the project serves as a focal point for cultural activities and community engagement, designed to respond to the city’s dynamic cultural landscape. The architects intended to create a space that fosters creativity, collaboration, and interaction while embodying the vibrancy associated with Japanese pop culture.
## Structural Composition
The building's design features a bold, geometric form characterized by an inclined roof and expansive glass façades, allowing natural light to fill the interior spaces. Supported by a steel framework with diagonal bracing, the structure combines aesthetic appeal with stability and durability. The innovative design reflects a modern approach to architecture, encouraging discussions about form and functionality.
## Materiality and Spatial Organization
The material selection plays a critical role in defining the project's identity. Extensive use of glass enhances transparency and connects the interior with the exterior environment, while steel provides the necessary strength to support the unique slanted design. Concrete forms the foundational elements, ensuring a strong base. The interior features vibrant textile installations that add visual interest to public spaces.
The layout emphasizes open, multifunctional areas that facilitate a range of activities, from exhibitions to workshops. Surrounding outdoor spaces promote community interaction and provide areas for relaxation, reinforcing the project’s role as a community hub. The integration of color, dynamic patterns, and innovative structural dynamics not only honors cultural expressions but also distinguishes the building within Tokyo's architectural context.