5 key facts about this project
### Architectural Design Report: House of the Future
#### Overview
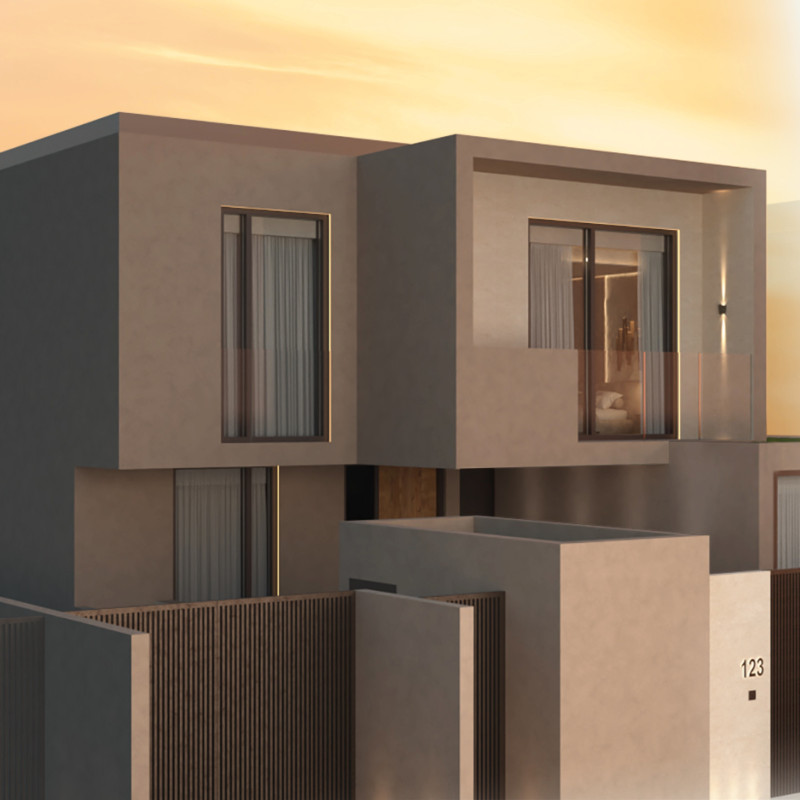
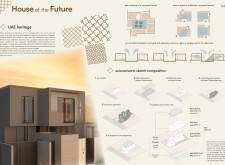
Located in the United Arab Emirates, this contemporary residential project merges traditional Emirati architectural elements with modern design principles. The structure is intended to create a functional and aesthetically pleasing environment that respects cultural heritage while addressing contemporary living needs. Central to the design is a courtyard that not only facilitates social interaction but also enhances privacy and air circulation, adhering to climate-responsive architectural practices.
#### Spatial Organization
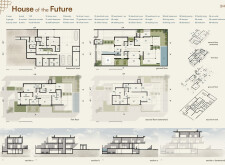
The residence features a multi-level layout organized into distinct functional zones:
- **Family Zone**: A welcoming area designed for everyday family activities.
- **Social Zone**: Dedicated spaces for entertaining guests, reflecting cultural values around hospitality.
- **Service Zone**: Includes essential functional areas such as laundry and storage, strategically placed for efficiency.
Key architectural elements include courtyards that enhance natural light and air flow, while a dynamic facade, achieved through careful volumetric geometry, adds visual richness to the design.
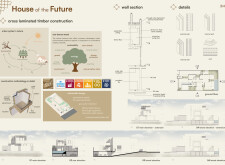
#### Materiality and Sustainability
Material selection plays a critical role in aligning the project with sustainable practices. Eco-friendly materials such as Cross Laminated Timber (CLT) and stone cladding were chosen for their structural integrity and cultural resonance. Glass is utilized extensively to foster connections between indoor and outdoor spaces, enhanced by aluminum venetian blinds for energy efficiency. The implementation of photovoltaic panels and water management systems underscores the commitment to sustainable energy and water usage. Additionally, energy-efficient fixtures help reduce the overall carbon footprint.
The design integrates features prioritizing privacy and community engagement, including high windows that limit sightlines into private areas and communal spaces that encourage social interaction. The overall design responds effectively to the harsh UAE climate, ensuring comfort and functionality throughout the year.