5 key facts about this project
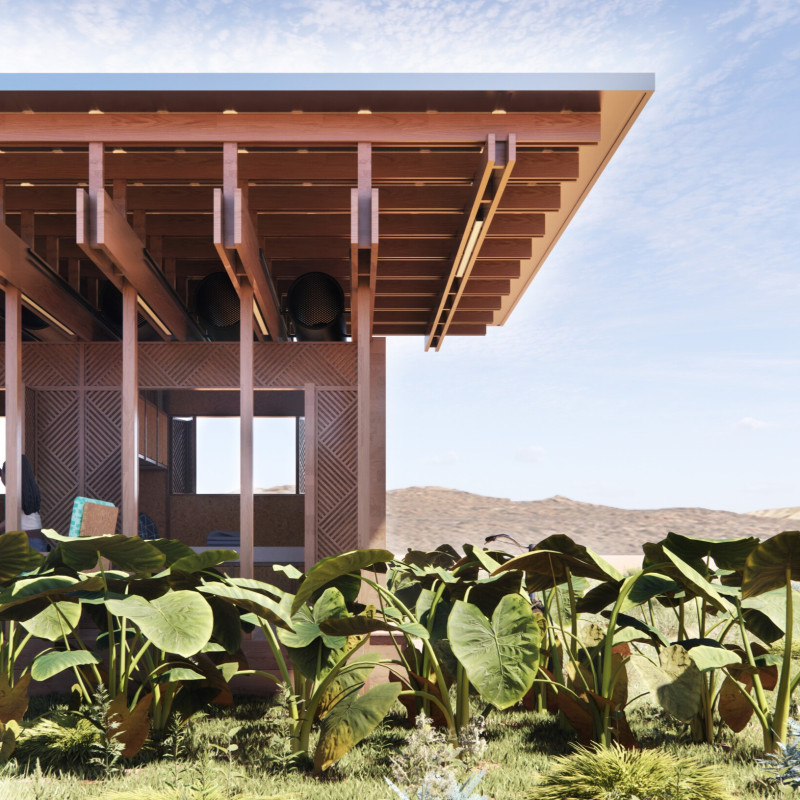
The Anti-Desertification House is located in sub-Saharan Africa, an area acutely affected by climate change and desertification. With an intent to create sustainable living environments that harmonize human needs with ecological preservation, the project employs innovative architectural methods to address water scarcity and promote resilience. By integrating bioclimatic principles, the design fosters energy efficiency and adaptability, aligning the built environment with natural systems.
### Design Framework and Material Utilization
The structural framework primarily consists of timber, selected for its low thermal mass, with a secondary support system that minimizes heat absorption and maximizes shade. The large overhanging roof design facilitates natural ventilation, reducing the reliance on mechanical cooling. Composite materials and locally sourced natural substances form the walls, which feature intricate lattice patterns that enhance airflow and thermal efficiency. This approach balances strength and sustainability, employing engineered wood to ensure durability while maintaining eco-friendly standards.
### Sustainable Practices and Functional Adaptability
Water management is a key focus, incorporating rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and advanced filtration systems to support sustainable water use in arid climates. The house features photovoltaic panels aimed at achieving energy neutrality, supplemented by storage solutions to regulate energy consumption effectively. The spatial configuration is modular, allowing for reconfiguration to meet evolving community needs. Communal areas promote social interaction, while private spaces incorporate large windows to capture natural light and views, thus fostering an inclusive and engaging living environment. This design exemplifies a commitment to ecological responsibility and community enhancement in one of the world's most vulnerable regions.