5 key facts about this project
## Location and Design Intent
The Moon House is situated in Dubai, an environment characterized by unique climatic challenges and urban dynamics. This residential design integrates contemporary architectural principles with sustainability and cultural significance. The project's framework emphasizes energy efficiency, material innovation, and spatial organization, making it relevant to both its geographical context and broader discussions on sustainable living.
## Form and Cultural Context
### Architectural Expression
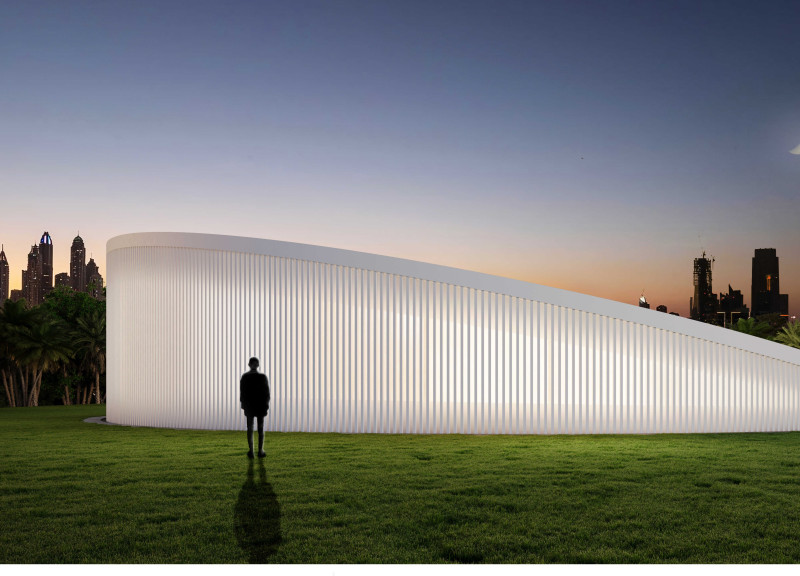
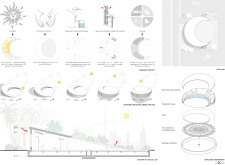
The structure is defined by a crescent shape, which serves both aesthetic and functional roles. This form optimizes solar absorption and natural ventilation, essential in a hot climate. The curvature fosters an organic connection with the surrounding vegetation and urban skyline, creating a cohesive visual narrative within its context.
### Cultural Significance
The crescent motif is deeply embedded in Arab culture, symbolizing renewal and fertility. This connection enhances the design's significance, integrating cultural narratives into the residential experience.
## Material Selection and Sustainability
### Key Materials
The construction employs prefabricated steel components, facilitating rapid assembly and disassembly. White photovoltaic panels adorn the roof, capturing solar energy and supporting the project's sustainability goals. The incorporation of glass and wood in the facades fosters an indoor-outdoor relationship while allowing natural light to permeate the living spaces, enhancing thermal comfort with wooden finishes that add warmth.
### Sustainable Strategies
The residence features a rotational mechanism, enabling it to adjust its orientation to maximize solar energy utilization throughout the day. A lithium-ion battery system efficiently stores energy, contributing to a self-sufficient power supply. Rainwater harvesting systems are integrated for irrigation and cooling purposes, aimed at minimizing the building's ecological impact. Additionally, passive ventilation strategies are employed to optimize airflow, further enhancing occupant comfort while reducing cooling energy demands.
## Spatial Configuration and User Experience
### Interior Layout
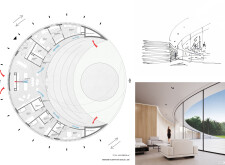
The internal organization prioritizes functionality and intimacy, with central communal spaces designed to facilitate interactions among residents. Distinct zoning for private sleeping quarters ensures individual privacy while maintaining overall community cohesion. The ground floor plan encompasses approximately 283.15 m², efficiently allocating areas for living rooms, bedrooms, bathrooms, and utility spaces.
### Connectivity and Natural Light
Large windows and an open layout enhance spatial continuity and natural lighting, providing panoramic views of both the lush landscape and Dubai’s urban environment. This design approach fosters an atmosphere of openness and integration with the external surroundings, contributing significantly to the overall user experience.