5 key facts about this project
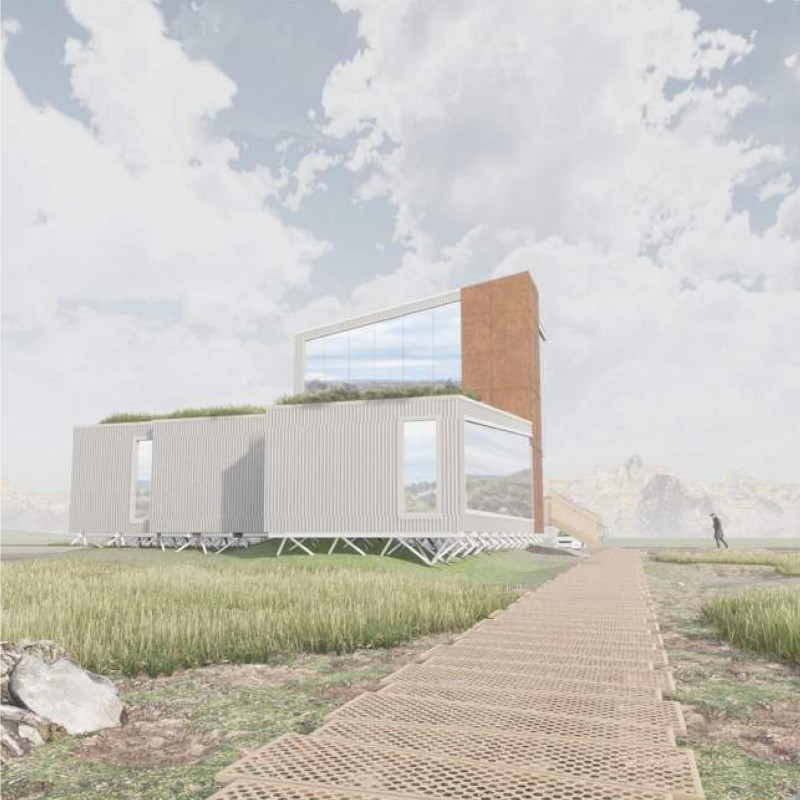
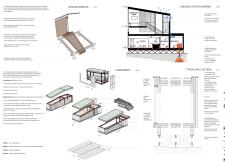
The Tektonisk Tower is an architectural project located in northeastern Iceland, designed to function as a visitor center and observation point. It aims to enhance public access to the stunning geological features of the region, specifically the Grjótagjá caves and nearby Mývatn. This project embodies a synergy between architecture and its natural context, promoting exploration and education about the unique geological landscapes of Iceland.
The design is characterized by modular forms that facilitate interaction with the environment while maintaining a cohesive visual identity. The structure’s massing is carefully composed to respond to the surrounding topography, emphasizing the geological context through its form and materials. The building materials were selected not only for aesthetic appeal but also for their performance under Iceland's variable climate conditions.
Integration of Function and Space
The Tektonisk Tower serves multiple functions, including a café, information center, and observation deck. The layout is organized into distinct zones that guide visitors through the space, encouraging movement and engagement with the natural landscape. The visitor center includes large windows that frame breathtaking views of the geological formations, creating visual connections between the interior spaces and the outdoor environment. This intentional design fosters a sense of place and orientation, enhancing the overall visitor experience.
The observation tower is a key component of the project, elevating its users above the landscape to provide panoramic views of the surrounding area. This design aspect is not only functional but also educational, allowing visitors to appreciate the geological features from an elevated perspective. The incorporation of walking paths around the building enhances accessibility and promotes exploration of the surrounding natural features.
Innovative Material Choices and Sustainable Practices
The Tektonisk Tower utilizes a combination of corten steel, prefabricated aluminum cladding, and local wooden materials to create a durable and visually coherent structure. Corten steel, with its distinctive weathered appearance, integrates well with the rugged Icelandic landscape while ensuring longevity against harsh weather conditions. The aluminum cladding contributes to the building’s lightweight design, minimizing its impact on the site.
Sustainability is a core principle of this architectural project. The building employs geothermal heating and cooling systems, taking advantage of the abundant geothermal energy available in Iceland. Rainwater collection systems further reduce environmental impact and enhance the building’s self-sufficiency. The green roof integrates local vegetation, providing insulation and promoting biodiversity in the area.
The Tektonisk Tower stands out for its integration of architecture and geology, facilitating a deeper understanding of the region's unique landscape. Its thoughtful design and sustainable practices make it an exemplary model for future projects in environmentally sensitive areas.
For a detailed understanding of the architectural decisions and design processes involved in the Tektonisk Tower, readers are encouraged to explore the architectural plans, sections, and designs that provide further insights into this project and its innovative approaches.